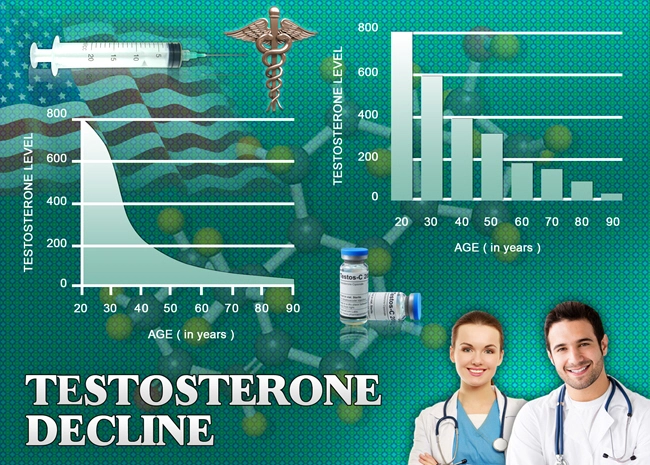
Introduction
In the bustling rhythm of modern American life, shift work has become a common necessity for many industries, including healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing. While this work pattern offers flexibility and meets the demands of a 24/7 economy, it poses significant health challenges, particularly for men. Recent studies have begun to unravel the connection between shift work and testosterone levels, shedding light on the potential risk of developing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome (TDS) among American males.
Understanding Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome
Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome, also known as hypogonadism, is a clinical condition characterized by low levels of testosterone and associated symptoms such as decreased libido, fatigue, depression, and reduced muscle mass. In the United States, TDS affects a significant portion of the male population, with prevalence increasing with age. However, emerging research suggests that lifestyle factors, including shift work, may contribute to the development of this syndrome at a younger age.
The Impact of Shift Work on Testosterone Levels
Shift work disrupts the body's natural circadian rhythms, leading to a cascade of physiological changes. One of the most concerning effects is the alteration in hormone production, particularly testosterone. Studies have shown that men working night shifts or rotating shifts experience a significant decrease in testosterone levels compared to those working regular daytime hours.
The mechanism behind this phenomenon is multifaceted. Firstly, exposure to light at night suppresses melatonin production, which in turn affects the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), a key regulator of testosterone. Secondly, the irregular sleep patterns associated with shift work lead to chronic sleep deprivation, which is known to lower testosterone levels. Finally, the stress and lifestyle changes that often accompany shift work, such as poor diet and lack of exercise, further exacerbate the problem.
Real-World Implications for American Males
For American men engaged in shift work, the risk of developing TDS is not just a theoretical concern but a tangible health issue. A study conducted by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health found that male shift workers in the U.S. reported higher incidences of symptoms associated with low testosterone, including decreased energy levels and sexual dysfunction.
The implications of these findings are profound. Men working non-traditional hours may find themselves at a higher risk of developing TDS, which can impact their quality of life and overall health. Moreover, the economic burden of managing TDS, including medical consultations and potential hormone replacement therapy, adds another layer of concern for affected individuals.
Strategies for Mitigating the Risk
While the link between shift work and testosterone deficiency is clear, there are steps that American males can take to mitigate this risk. Firstly, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, even on days off, can help stabilize circadian rhythms. Secondly, exposure to natural light during the day and minimizing light exposure at night can support healthy melatonin production.
In addition, adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support testosterone production (such as zinc and vitamin D), and stress management techniques can all contribute to maintaining optimal hormone levels. For those already experiencing symptoms of TDS, consulting a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and potential treatment options is essential.
Conclusion
As the prevalence of shift work continues to rise in the United States, understanding its impact on testosterone levels and the risk of developing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome becomes increasingly important. American males engaged in shift work must be aware of these health risks and take proactive steps to safeguard their well-being. By prioritizing sleep, nutrition, and overall lifestyle, men can navigate the challenges of shift work while maintaining their hormonal health and vitality.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Managing Testosterone Deficiency in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testosterone and Risk of Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Symptoms, Importance of Regular Check-ups, and Treatment Benefits [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Energy Impact [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Stress and Testosterone Deficiency: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Hormone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Muscle Mass and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins and Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Public Health Implications [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts, Management, and Prostate Health Considerations [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Skin Health and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management of Joint Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Zinc's Vital Role in Treating Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Mood Disorders: Insights and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- High-Fat Diets and Testosterone: Impacts and Dietary Recommendations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Health Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Diet Soda's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Weight Training Benefits for Men with Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Depression: Understanding the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Hearing Loss in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact on Libido and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Sleep Apnea: Interconnected Health Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Anemia: Understanding the Link and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Body Composition in American Males: Health Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Magnesium's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Understanding Its Link to Hair Loss in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness and Testosterone Deficiency: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management in American Athletes [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in Men: Impacts on Vision and Eye Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Pesticide Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Boron's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in U.S. Males: A Promising Adjunct [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Kidney Health Risks in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Memory and Cognitive Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Dental Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Soy Consumption and Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Blue Light Exposure and Testosterone Levels: Managing TDS in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Increased Gallbladder Disease Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Plasticizers' Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Men: An Emerging Concern [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Heavy Metal Exposure and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Liver Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Promising Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Air Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- EMFs and Testosterone: Understanding Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for Male Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Thyroid Function: Interplay and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Fenugreek: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Pancreatic Health: Implications for American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact of Adrenal Health and Holistic Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Noise Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Tribulus Terrestris: A Natural Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Parathyroid Health: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Hypothalamic Role and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Fluoride Exposure and Testosterone Levels: Implications for TDS in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Pineal Gland's Role in Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- DHEA Supplementation: A Promising Treatment for Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Ginseng's Potential Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in U.S. Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- BPA Exposure Linked to Lower Testosterone Levels in American Men: TDS Implications [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Respiratory Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Phthalates' Role in Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- PFC Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Gastrointestinal Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts and Management of Urinary Health [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impact of Endocrine Disruptors and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Autoimmune Disorders: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Cordyceps: A Natural Ally in Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Metabolic Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Shilajit's Potential in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Neurological Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Triclosan Exposure and Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Parabens' Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Implications for TDS [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Phytoestrogens' Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Organophosphate Pesticides Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Multivariate Analysis [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- TDS Impact on American Males: Age-Specific Effects and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Twin Studies Reveal Genetic and Environmental Factors in Testosterone Deficiency Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]