Introduction to Human Growth Hormone and Its Synthetic Forms
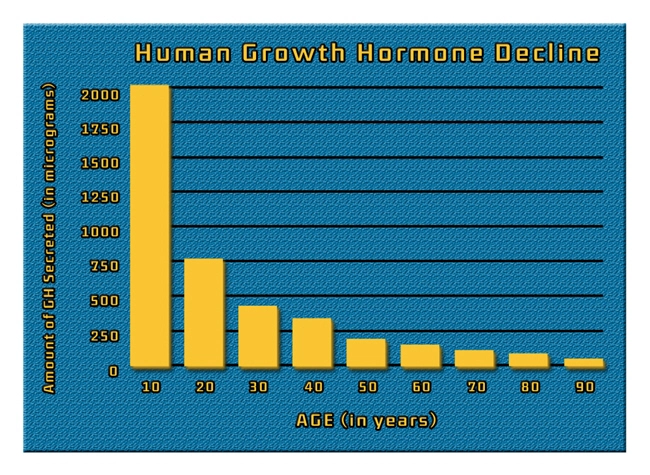
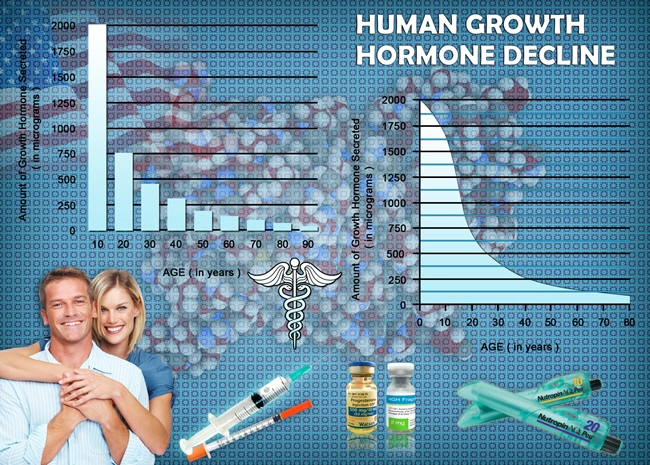
Human Growth Hormone (HGH) is a pivotal hormone produced by the pituitary gland, playing crucial roles in growth, body composition, cell repair, and metabolism. Synthetic HGH has been widely used in medicine to treat various disorders, including growth hormone deficiency, Turner's syndrome, and muscle wasting diseases associated with HIV/AIDS. However, the use of synthetic HGH is not without risks, including joint and muscle pain, edema, and increased risk of diabetes and heart disease.
Sermorelin: The Natural Stimulator of HGH
Sermorelin, a synthetic form of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), represents a safer, more natural alternative. Unlike synthetic HGH, which directly supplements the hormone, Sermorelin stimulates the pituitary gland to increase its own production of HGH. This method of enhancing HGH levels is more in tune with the body's natural rhythms and feedback systems.
The Mechanism of Sermorelin
Sermorelin is composed of the first 29 amino acids of the naturally occurring GHRH. These are the most potent segments for stimulating HGH secretion. By mimicking natural GHRH, Sermorelin binds to specific receptors on the pituitary gland, promoting HGH production. This not only helps in maintaining the natural pulsatile release of HGH but also helps in regulating its level through the body's inherent feedback mechanisms, thus minimizing the risks associated with high levels of synthetic HGH.
Benefits of Sermorelin Over Synthetic HGH
Sermorelin offers several advantages over synthetic HGH. First, it supports natural HGH production, which is regulated by the body's needs, reducing the risk of overdose and side effects. Additionally, Sermorelin can improve sleep cycles and enhance the quality of REM sleep, further supporting overall health and well-being. It also supports more natural growth patterns in children with growth hormone deficiencies, as opposed to the sometimes erratic growth patterns caused by synthetic HGH.
Clinical Applications and Safety
Clinically, Sermorelin has been used to treat children with growth hormone deficiency and is also considered for adults experiencing age-related declines in growth hormone. Its use is generally considered safe, with fewer and less severe side effects compared to synthetic HGH. Common side effects include flushing, headache, and nausea, which typically resolve with continued use.
Conclusion: The Future of Hormone Therapy
As research continues, Sermorelin may offer a broader range of applications. Its ability to naturally stimulate HGH production makes it a promising candidate for anti-aging treatments and for enhancing overall vitality. Moreover, its safety profile makes it a preferable choice for long-term therapy in managing conditions associated with low levels of HGH. In the landscape of hormone replacement therapy, Sermorelin stands out as a natural, effective, and safe alternative, heralding a new era in endocrine health management. As healthcare continues to move towards more holistic and patient-centered approaches, Sermorelin's role is likely to expand, offering patients a natural and balanced option to manage their hormone levels.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Unlocking the Secrets of Sermorelin: An Ultimate Guide to Amplifying Body's Own Growth [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Rediscovering Vitality: Sermorelin's Role in Revitalizing Your Body's Growth Hormone Function [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Rediscovering the Fountain of Youth: Sermorelin Peptide in Anti-Aging Therapy [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Decoding the Wonder Drug: Sermorelin's Modern Medical Revolution [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Celebration of Nature’s Wisdom: How Sermorelin Boosts Your Body’s Innate Growth Stimulus [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Embracing the Innovation in Hormonal Health: Unveiling the Potency of Sermorelin [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Unraveling the Miraculous Age-Reversal Secret: The Role of Sermorelin [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]