Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
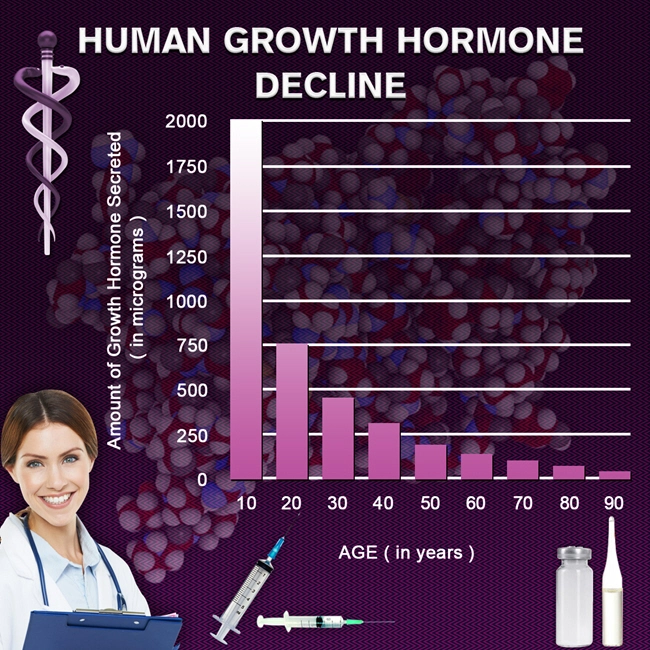
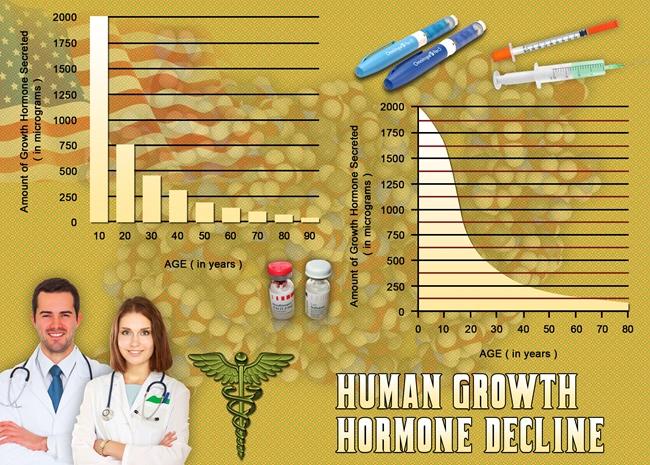
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition where the body does not produce enough testosterone due to a problem with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, is increasingly recognized as a significant health issue among American males. This condition can lead to a myriad of symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, and mood disturbances, which can severely impact quality of life. Understanding and managing secondary hypogonadism is crucial for optimizing health outcomes and enhancing the well-being of affected individuals.
Causes and Diagnosis
The etiology of secondary hypogonadism can be multifaceted, often stemming from conditions such as pituitary disorders, hypothalamic diseases, or even the use of certain medications. Accurate diagnosis is paramount and typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history and physical examination. Laboratory tests measuring serum testosterone levels, along with luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), are essential for confirming the diagnosis. Imaging studies, such as MRI of the brain, may be warranted to identify any structural abnormalities in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
Impact on American Males
In the United States, secondary hypogonadism affects a significant portion of the male population, with prevalence rates increasing with age. The condition's impact extends beyond physical symptoms, influencing mental health and overall life satisfaction. American males with secondary hypogonadism may experience diminished sexual function, reduced muscle mass, and increased body fat, which can contribute to metabolic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Addressing this condition is not only about alleviating symptoms but also about preventing long-term health complications.
Treatment Approaches
Effective management of secondary hypogonadism involves a tailored approach, considering the underlying cause and individual patient needs. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a cornerstone of treatment, aimed at restoring testosterone levels to normal ranges. Various formulations of testosterone, including gels, injections, and patches, are available, each with its own set of advantages and potential side effects. It is crucial for patients to work closely with healthcare providers to monitor hormone levels and adjust treatment as necessary.
In cases where secondary hypogonadism is caused by a treatable condition, such as a pituitary tumor, addressing the underlying issue may resolve the hormonal imbalance. Surgical intervention or radiation therapy may be considered, depending on the specific diagnosis. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can complement medical treatments and improve overall health outcomes.
Psychological and Social Considerations
The psychological impact of secondary hypogonadism should not be underestimated. Many American males may experience feelings of embarrassment or frustration due to the symptoms of this condition, which can affect personal relationships and professional life. Support from mental health professionals, as well as peer support groups, can be invaluable in helping individuals cope with the emotional aspects of secondary hypogonadism. Open communication with partners and family members is also essential for fostering understanding and support.
Future Directions and Research
Ongoing research into secondary hypogonadism continues to shed light on its pathophysiology and potential new treatment modalities. Advances in genetic testing and personalized medicine hold promise for more targeted and effective therapies. As awareness of this condition grows, it is hoped that more American males will seek timely diagnosis and treatment, leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism represents a significant health challenge for American males, but with appropriate diagnosis and management, its impact can be mitigated. By understanding the causes, seeking timely treatment, and addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition, affected individuals can achieve optimal health and well-being. As research progresses, the future looks promising for those living with secondary hypogonadism, offering hope for even more effective and personalized care.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Psychological Impacts on American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Support Systems Crucial for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Pituitary Gland's Role and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Understanding and Managing the Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Factors Driving Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Importance of Early Detection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders in American Men: Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men's Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Fatigue in American Males with Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Factors and Medical Interventions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: A Critical Connection for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Impacts, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Treatment Implications in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Strength and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Insights and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Causes, Effects, and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Hormonal Therapies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Role of Diet in Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Health and Relationships in America [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Holistic Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management for American Men's Daily Life [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Personalized Treatment [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Vitality and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Impact and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Boosting Testosterone Naturally [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Impacts, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]