Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
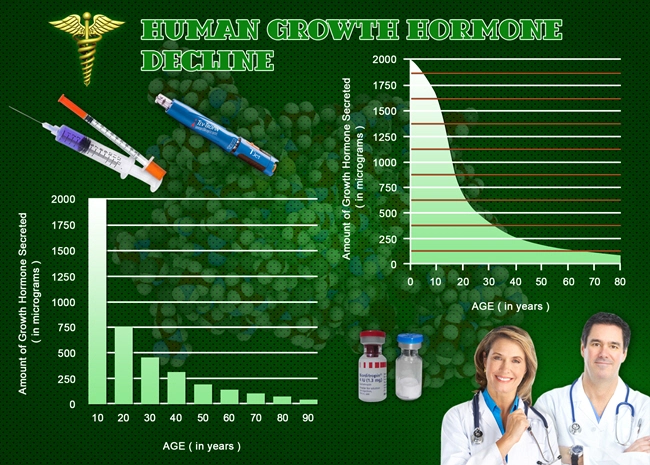
Secondary hypogonadism, also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, is a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to a dysfunction in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. This condition affects a significant number of American males, leading to a variety of symptoms that can impact their quality of life. Understanding and managing secondary hypogonadism is crucial for restoring hormonal balance and improving overall health.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of secondary hypogonadism can be subtle and may include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, loss of muscle mass, and mood changes. Due to the non-specific nature of these symptoms, diagnosis can be challenging. A thorough evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests measuring testosterone and gonadotropin levels, is essential for an accurate diagnosis. In secondary hypogonadism, testosterone levels are low, while gonadotropin levels (LH and FSH) are either normal or low, distinguishing it from primary hypogonadism.
Underlying Causes
Secondary hypogonadism can arise from various underlying causes. Common etiologies include pituitary tumors, genetic disorders such as Kallmann syndrome, obesity, chronic opioid use, and systemic illnesses. Identifying the root cause is vital for tailoring an effective treatment plan. In some cases, addressing the underlying condition can lead to the resolution of hypogonadism without the need for long-term hormonal therapy.
Treatment Options
The primary goal of treating secondary hypogonadism is to restore testosterone levels to the normal range and alleviate associated symptoms. Treatment options vary based on the underlying cause and individual patient factors.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
For many American males with secondary hypogonadism, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is the cornerstone of treatment. HRT can be administered through various methods, including intramuscular injections, transdermal patches, gels, or pellets. Each method has its advantages and considerations, and the choice depends on patient preference, lifestyle, and insurance coverage. Regular monitoring of testosterone levels and symptoms is essential to ensure optimal dosing and minimize potential side effects.
Gonadotropin Therapy
In cases where the goal is to preserve fertility, gonadotropin therapy may be preferred. This treatment involves the administration of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to stimulate the testes to produce testosterone and sperm. Gonadotropin therapy is particularly beneficial for men who wish to conceive and can be used in conjunction with HRT in some cases.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing secondary hypogonadism. Weight loss, regular exercise, and cessation of opioid use can significantly improve testosterone levels in some men. A balanced diet rich in nutrients and adequate sleep also contribute to overall hormonal health.
Monitoring and Long-term Management
Ongoing monitoring is essential for men receiving treatment for secondary hypogonadism. Regular follow-up appointments allow healthcare providers to assess treatment efficacy, adjust dosages as needed, and monitor for potential side effects such as erythrocytosis, sleep apnea, and prostate issues. Long-term management may involve periodic reassessment of the underlying cause and consideration of treatment discontinuation if the condition resolves.
Psychological and Emotional Support
The impact of secondary hypogonadism extends beyond physical symptoms, often affecting mental health and relationships. Providing psychological and emotional support is crucial for American males navigating this condition. Counseling, support groups, and open communication with partners can help address the emotional challenges associated with hypogonadism and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism presents a complex challenge for American males, but with a comprehensive approach to treatment, significant improvements in quality of life can be achieved. By understanding the symptoms, identifying underlying causes, and implementing tailored treatment plans, healthcare providers can help men regain hormonal balance and vitality. As research continues to advance, the future holds promise for even more effective strategies in managing this condition.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Psychological Impacts on American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Support Systems Crucial for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Pituitary Gland's Role and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Understanding and Managing the Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Factors Driving Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Importance of Early Detection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders in American Men: Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men's Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Fatigue in American Males with Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Factors and Medical Interventions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: A Critical Connection for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Impacts, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Treatment Implications in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Strength and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Insights and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Causes, Effects, and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Hormonal Therapies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Role of Diet in Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Health and Relationships in America [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Holistic Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management for American Men's Daily Life [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Personalized Treatment [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Vitality and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Impact and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Boosting Testosterone Naturally [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]