Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition where the body fails to produce adequate levels of testosterone due to a dysfunction in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has been increasingly recognized in American males. This condition can lead to a myriad of health issues, one of which is anemia. Anemia, characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin, can manifest in symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Understanding the interplay between these two conditions is crucial for American men seeking to maintain their health and vitality.
The Pathophysiology of Secondary Hypogonadism
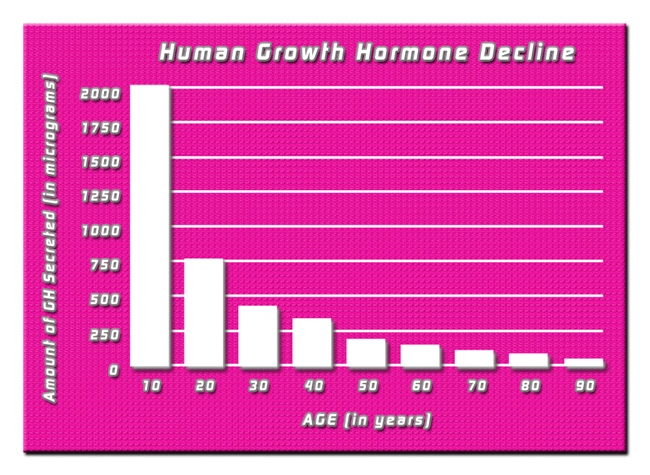
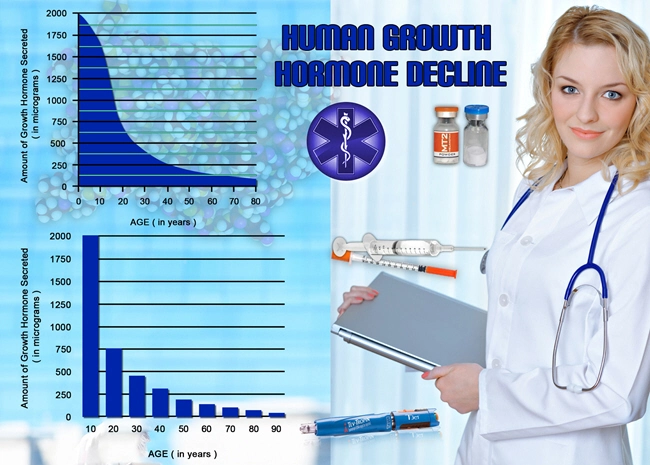
Secondary hypogonadism arises when the hypothalamus or pituitary gland does not function properly, leading to reduced secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) or luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones are essential for stimulating the testes to produce testosterone. Without adequate testosterone, men may experience a range of symptoms including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and muscle weakness. Moreover, testosterone plays a pivotal role in erythropoiesis, the process of red blood cell production, which when impaired, can lead to anemia.
The Connection to Anemia
Testosterone is known to stimulate the production of erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone produced by the kidneys that prompts the bone marrow to produce red blood cells. In cases of secondary hypogonadism, the reduced levels of testosterone can lead to decreased EPO production, subsequently resulting in anemia. This form of anemia, often referred to as hypogonadal anemia, is particularly relevant for American males who may be at risk due to lifestyle factors, obesity, or underlying medical conditions.
Recognizing the Symptoms
American males with secondary hypogonadism may experience symptoms that overlap with those of anemia, making diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms include fatigue, decreased energy levels, and mood changes. Additionally, men may notice a decline in physical performance and endurance, which can significantly impact their quality of life. It is essential for men to seek medical evaluation if they experience these symptoms, as early detection and treatment can mitigate the progression of both conditions.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing secondary hypogonadism and anemia requires a comprehensive approach. Blood tests to measure testosterone levels, LH, FSH, and complete blood counts are fundamental. Additionally, assessing iron levels and other markers of anemia can provide a clearer picture of a patient's health status. American males should consult with healthcare professionals who can tailor diagnostic tests to their specific symptoms and medical history.
Treatment Strategies
Treatment for secondary hypogonadism typically involves testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), which can help restore normal testosterone levels and alleviate symptoms. For men with concurrent anemia, TRT can also improve red blood cell production. However, TRT must be administered under strict medical supervision due to potential side effects and the need for regular monitoring. In some cases, addressing underlying causes such as obesity or hormonal imbalances can also improve outcomes.
Lifestyle and Preventive Measures
American males can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing secondary hypogonadism and anemia. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support overall hormonal health. Additionally, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and managing stress effectively can contribute to better health outcomes.
Conclusion
The relationship between secondary hypogonadism and anemia is a critical consideration for American males. By understanding the mechanisms behind these conditions and recognizing their symptoms, men can seek timely medical intervention. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments, it is possible to manage these conditions effectively and maintain a high quality of life. As research continues to evolve, American males should stay informed and work closely with healthcare providers to address their health needs comprehensively.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Psychological Impacts on American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Support Systems Crucial for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Pituitary Gland's Role and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Factors Driving Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Importance of Early Detection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders in American Men: Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men's Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Fatigue in American Males with Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Factors and Medical Interventions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: A Critical Connection for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Impacts, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Treatment Implications in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Strength and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Insights and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Causes, Effects, and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Hormonal Therapies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Role of Diet in Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Health and Relationships in America [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Holistic Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management for American Men's Daily Life [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Personalized Treatment [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Vitality and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Impact and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Boosting Testosterone Naturally [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]