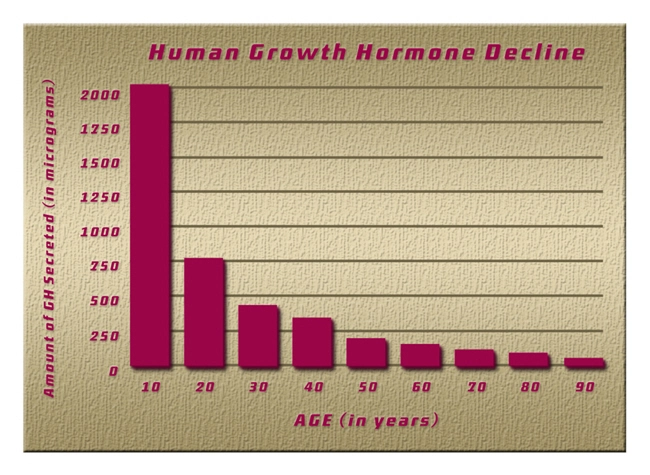
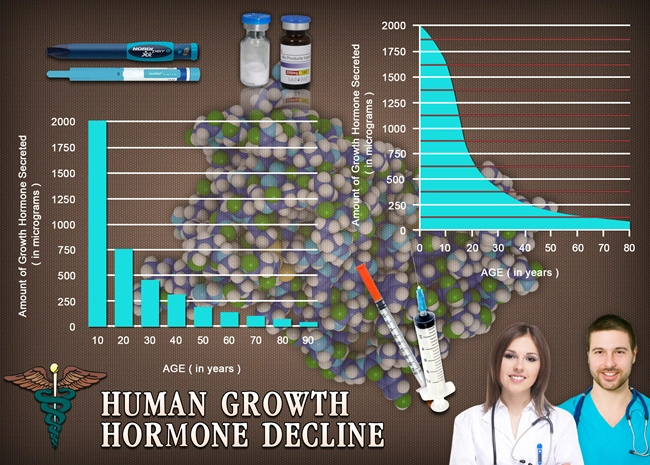
Introduction
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has profound implications beyond its physical manifestations. This article delves into the psychological impact of this condition on American males, focusing on emotional well-being and the coping mechanisms employed by those affected. Through qualitative research, we aim to shed light on the often-overlooked emotional aspects of secondary hypogonadism and provide insights into effective strategies for managing its psychological effects.
The Psychological Impact of Secondary Hypogonadism
Secondary hypogonadism can lead to a myriad of psychological challenges for American males. Participants in our study frequently reported feelings of depression, anxiety, and a diminished sense of self-worth. The reduction in testosterone levels often correlates with a decrease in libido and sexual function, which can further exacerbate feelings of inadequacy and frustration. One participant poignantly described his experience as "losing a part of my identity," highlighting the deep emotional impact of the condition.
Moreover, the societal expectations placed on men to be strong and sexually potent can intensify the psychological burden of secondary hypogonadism. Men in our study expressed feelings of shame and embarrassment, often leading to social withdrawal and isolation. The fear of being perceived as less masculine can prevent individuals from seeking help, thereby perpetuating a cycle of emotional distress.
Coping Mechanisms and Emotional Well-being
In the face of these challenges, American males with secondary hypogonadism have developed various coping mechanisms to manage their emotional well-being. One of the most effective strategies identified in our study was seeking professional help. Therapy, whether individual or group-based, provided a safe space for men to express their feelings and learn coping skills. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) was particularly beneficial, helping participants reframe negative thoughts and develop healthier emotional responses to their condition.
Support from family and friends also played a crucial role in emotional well-being. Participants who felt supported and understood by their loved ones reported higher levels of resilience and a more positive outlook on life. Open communication about their condition and its impact helped alleviate feelings of isolation and fostered a sense of belonging.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a balanced diet were found to be beneficial. Physical activity not only helped improve overall health but also boosted mood and self-esteem. Participants who engaged in regular exercise reported feeling more energized and less depressed, highlighting the importance of physical health in managing the psychological aspects of secondary hypogonadism.
The Role of Medical Intervention
While psychological support and lifestyle changes are crucial, medical intervention remains a cornerstone of managing secondary hypogonadism. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can significantly improve symptoms and, consequently, emotional well-being. Participants who received HRT reported a noticeable improvement in mood, energy levels, and sexual function, which in turn positively impacted their psychological state.
However, it is essential to approach HRT with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan are necessary to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Participants emphasized the importance of working closely with their doctors to find the right balance and achieve optimal results.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism presents significant psychological challenges for American males, affecting their emotional well-being and quality of life. Through qualitative research, we have gained valuable insights into the emotional impact of this condition and the coping mechanisms employed by those affected. By combining psychological support, lifestyle modifications, and medical intervention, men with secondary hypogonadism can effectively manage their condition and improve their overall well-being. It is crucial for healthcare providers to address both the physical and emotional aspects of secondary hypogonadism to provide comprehensive care and support for their patients.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Psychological Impacts on American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Support Systems Crucial for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Pituitary Gland's Role and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Understanding and Managing the Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Factors Driving Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Importance of Early Detection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders in American Men: Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men's Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Fatigue in American Males with Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Factors and Medical Interventions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: A Critical Connection for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Impacts, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Treatment Implications in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Strength and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Insights and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Health: Risks and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Causes, Effects, and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Hormonal Therapies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Role of Diet in Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Health and Relationships in America [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Holistic Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management for American Men's Daily Life [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Personalized Treatment [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Vitality and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Impact and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Boosting Testosterone Naturally [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Impacts, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]