Introduction to Bodybuilding and Metabolism
Bodybuilding, a popular sport and fitness regimen among American males, involves rigorous training and dietary adjustments aimed at enhancing muscle mass and reducing body fat. From a biologist's perspective, understanding the metabolic effects of bodybuilding is crucial for optimizing health and performance. This article delves into the intricate metabolic changes that occur in response to bodybuilding practices, offering valuable insights for those engaged in this demanding physical pursuit.
The Role of Diet in Bodybuilding
Diet plays a pivotal role in bodybuilding, influencing the metabolic pathways that support muscle growth and fat loss. A typical bodybuilding diet is high in protein, which is essential for muscle repair and growth. Proteins are broken down into amino acids, which are then used to rebuild muscle fibers damaged during intense workouts. Additionally, carbohydrates are crucial for providing the energy needed for these workouts, while fats are necessary for hormonal balance and overall health.
Metabolic Adaptations to Resistance Training
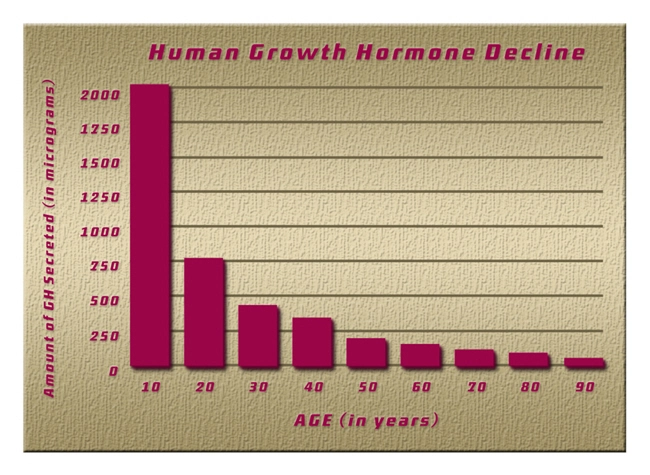
Resistance training, the cornerstone of bodybuilding, induces significant metabolic adaptations. When muscles are subjected to resistance, they undergo micro-tears, triggering a cascade of metabolic responses aimed at repair and growth. This process is mediated by anabolic hormones such as testosterone and growth hormone, which are elevated in response to resistance training. These hormones facilitate protein synthesis, leading to increased muscle mass over time.
Impact on Basal Metabolic Rate
Engaging in bodybuilding can lead to an increase in basal metabolic rate (BMR). BMR is the number of calories the body needs to maintain basic physiological functions at rest. As muscle mass increases, so does BMR, because muscle tissue requires more energy to maintain than fat tissue. This increase in BMR can help bodybuilders maintain a lean physique by burning more calories even when not exercising.
Glycogen Storage and Utilization
Bodybuilding also affects glycogen storage and utilization. Glycogen, the stored form of glucose, is primarily stored in the liver and muscles. During intense workouts, muscle glycogen is rapidly depleted, necessitating its replenishment through carbohydrate intake. This cycle of depletion and replenishment can enhance the body's ability to store and utilize glycogen more efficiently, which is beneficial for sustained performance during workouts.
Hormonal Fluctuations and Their Effects
The metabolic effects of bodybuilding are closely tied to hormonal fluctuations. In addition to anabolic hormones, bodybuilding can influence levels of cortisol, a stress hormone that can lead to muscle breakdown if chronically elevated. Balancing training intensity and recovery is crucial to managing cortisol levels and optimizing the anabolic environment necessary for muscle growth.
Nutrient Timing and Metabolic Efficiency
Nutrient timing is another critical aspect of bodybuilding that impacts metabolic efficiency. Consuming proteins and carbohydrates immediately after a workout can enhance muscle recovery and growth by providing the necessary building blocks and energy at the optimal time. This practice, known as nutrient timing, can maximize the metabolic benefits of bodybuilding by ensuring that nutrients are available when the body is most receptive to them.
Long-Term Metabolic Health Considerations
While bodybuilding can offer short-term metabolic benefits, it is important to consider its long-term impact on metabolic health. Chronic adherence to extreme diets and intense training regimens can lead to metabolic imbalances, such as insulin resistance and hormonal dysregulation. Therefore, it is essential for bodybuilders to adopt a balanced approach that includes periods of rest and varied nutrition to maintain long-term metabolic health.
Conclusion: Optimizing Bodybuilding for Metabolic Health
In conclusion, bodybuilding induces a range of metabolic effects that can enhance muscle growth and fat loss when managed correctly. American males engaged in bodybuilding should be aware of the importance of diet, resistance training, and nutrient timing in optimizing their metabolic health. By understanding and leveraging these metabolic dynamics, bodybuilders can achieve their fitness goals while maintaining overall health and well-being.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Unveiling the Synergy Between Body Building and Diabetes Control in American Males [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- The Therapeutic Impact of Bodybuilding on Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Enhancing Bodybuilding Performance and Injury Prevention: The Integral Role of Physical Therapy [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Nutrition for Successful Bodybuilding: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Body Building: A Strategic Approach to Combat Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: Impact on Health and Body Composition in American Males [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring the Cardiovascular Benefits of Bodybuilding for American Men [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Optimizing Orthopedic Health in Bodybuilding: Strategies to Prevent Injuries and Enhance Performance [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Nexus of Longevity and Body Building: Insights from Geriatric Medicine [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Dark Side of Bodybuilding: Risks and Consequences of Anabolic Steroid Use [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Endocrinological Blueprint of Bodybuilding: Hormones, Risks, and Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Mental Health: Self-Esteem, Stress Relief, and Social Bonds for American Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- The Impact of Bodybuilding on Sleep: A Comprehensive Analysis for American Males [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Unleashing the Power of Body Building: A Therapeutic Approach to Managing Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Potent Strategy for Hypertension Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Injury Prevention Strategies for American Male Bodybuilders: Expert Physiotherapy Insights [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Body Building Myths and Facts for American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Integrating Bodybuilding into Post-Surgical Rehabilitation for American Males: A Physician's Guide [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Therapeutic Strategy for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Competitive Bodybuilding: Health Risks and Mitigation Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Endocrine System: Hormones, Health Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Body Building: A Therapeutic Approach to Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Debunking Menstrual Cycle Myths: Optimizing Women's Bodybuilding Training [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Immunity: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Role in Enhancing Addiction Recovery for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Asthma and Bodybuilding: Safety, Benefits, and Program Tailoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Lifestyle Diseases in Bodybuilding: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Role in Enhancing Holistic Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Strategies for American Males to Combat Age-Related Muscle Loss [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Heart Health: Risks and Cardiologist's Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Prostate Health: Hormones, Supplements, and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding in Young Males: Benefits, Risks, and Safe Practices [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Essential Vitamins and Supplements for American Male Bodybuilders: Enhancing Muscle Growth and Performance [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Kidney Health in Bodybuilding: Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Orthostatic Hypotension in Bodybuilding: Risks, Symptoms, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Body Building: A Non-Pharmacological Approach to Managing Parkinson's in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Management: Body Building Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Natural Strategy for Arthritis Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Liquid Diets in Bodybuilding: Risks, Benefits, and Sustainable Alternatives [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Postnatal Recovery for New American Fathers: Physical and Psychological Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Benefits for American Males with COPD: Strength, Respiratory Health, and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Comprehensive Anti-Aging Strategy for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Gut Health in American Males: Clinical Insights and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Psychological Impact on American Teenage Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Strength Recovery in American Males Post-Chemotherapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Body Building Enhances Lung Function in American Males: A Respiratory Therapist's Insight [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Reduces Colon Cancer Risk in American Males: Diet, Hormones, and Fitness [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Essential Safety Guidelines for American Male Bodybuilders [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Immune Health: Optimal Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Male Menopause and Body Building: Strategies for Muscle Growth and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sickle Cell Disease and Body Building: Benefits, Risks, and Guidelines for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Body Building and Heart Health: Benefits and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: Building Mental Resilience and Fortitude in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Brain Health: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Body Building and Dementia Risk: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Approach for American Males with Chronic Degenerative Diseases [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Genetics in Bodybuilding: Optimizing Muscle Growth and Recovery for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Preventive Strategy for Musculoskeletal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hydration Strategies for American Male Bodybuilders: Enhancing Performance and Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Bone Density in American Males: Training and Nutrition Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Injury Prevention and Management Strategies for American Male Bodybuilders [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as Adjunct Therapy for Mood Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Therapeutic Tool for PTSD in American Males: Benefits and Implementation [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Life Expectancy: Benefits, Risks, and Balance for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Metabolism and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Medically Supervised Bodybuilding: A Safe Path to Fitness for American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Cardiovascular Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Hormones: Testosterone, Cortisol, and Growth Hormone Fluctuations [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Gut Health's Crucial Role in Bodybuilding for American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Recovery and Well-being Post Joint Replacement Surgery [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Stretching Essentials for American Male Bodybuilders: Enhancing Performance and Health [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as Effective Stress Management for American Males: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Enhancing Bodybuilding with Flexibility: Benefits and Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Therapeutic Approach to Managing Sciatica in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Structured Body Building: A Preventive Strategy for Low Back Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Approach to Managing ADHD in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Back Pain: Chiropractic Strategies for Prevention and Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Optimizing Protein Intake for Vegetarian Bodybuilding in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Safely During Partner's Pregnancy: Guidelines for Expectant Fathers [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Overexertion Risks and Safe Training Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]