Introduction
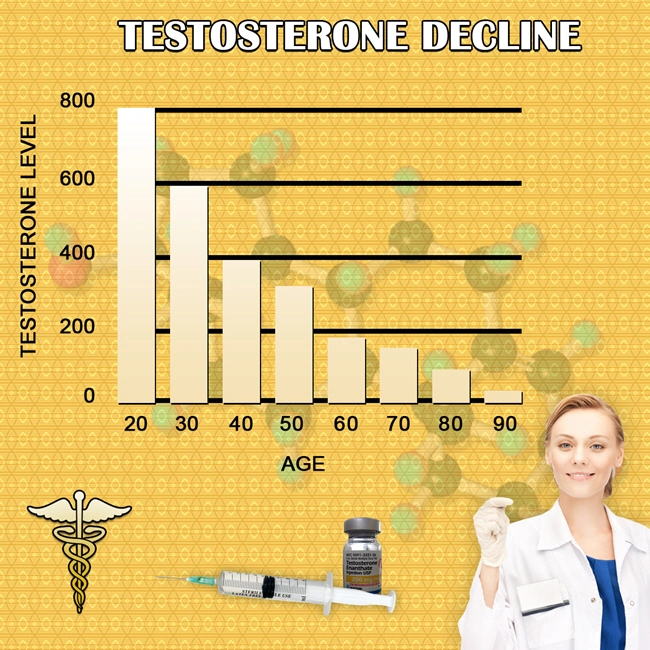
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including the maintenance of hematological health. Recent studies have begun to explore the association between low testosterone levels and the increased risk of hematological disorders among American men. This article delves into the current understanding of this relationship, highlighting the importance of monitoring and managing testosterone levels to mitigate potential health risks.
The Role of Testosterone in Hematopoiesis
Testosterone is not only essential for sexual development and function but also significantly influences hematopoiesis, the process of blood cell formation. It stimulates the production of erythropoietin, a hormone that promotes the creation of red blood cells. Consequently, a deficiency in testosterone can lead to a decrease in erythropoietin levels, potentially resulting in anemia and other hematological issues.
Epidemiological Evidence Linking Low Testosterone to Hematological Disorders
Several epidemiological studies have provided evidence supporting the link between low testosterone and hematological disorders. For instance, a study published in the *Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism* found that men with lower testosterone levels were at a higher risk of developing anemia. Similarly, research in the *American Journal of Hematology* indicated an association between hypogonadism and an increased incidence of thrombocytopenia and leukopenia.
Mechanisms Underlying the Association
The mechanisms through which low testosterone contributes to hematological disorders are multifaceted. One primary pathway involves the direct impact of testosterone on bone marrow function. Testosterone receptors are present in bone marrow cells, and their activation by testosterone promotes the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. When testosterone levels are low, these processes are impaired, leading to suboptimal blood cell production.
Additionally, low testosterone can indirectly affect hematological health by influencing other hormones and metabolic pathways. For example, reduced testosterone levels can lead to increased fat mass and insulin resistance, both of which are associated with inflammation and oxidative stress, further exacerbating hematological dysfunction.
Clinical Implications and Management Strategies
The clinical implications of the relationship between low testosterone and hematological disorders are significant, particularly for American men. Routine screening for testosterone levels in men presenting with hematological abnormalities may be warranted. Moreover, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) could be considered as a potential treatment option for those diagnosed with both low testosterone and hematological disorders.
However, the decision to initiate TRT should be made cautiously, taking into account the individual's overall health profile and potential risks associated with hormone therapy. Regular monitoring of hematological parameters and testosterone levels is essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of such interventions.
Future Research Directions
While the current evidence suggests a link between low testosterone and hematological disorders, further research is needed to fully elucidate the underlying mechanisms and to establish definitive clinical guidelines. Longitudinal studies that track changes in testosterone levels and hematological health over time could provide valuable insights. Additionally, randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of TRT on hematological outcomes in men with low testosterone are crucial to inform clinical practice.
Conclusion
The association between low testosterone and an increased risk of hematological disorders in American men underscores the importance of hormonal health in maintaining overall well-being. By recognizing and addressing low testosterone levels, healthcare providers can potentially mitigate the risk of developing serious hematological conditions. As research continues to unravel the complexities of this relationship, it is imperative that clinicians remain vigilant and proactive in managing testosterone levels in their male patients.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Environmental Toxins Linked to Low Testosterone in American Men: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone: Symptoms, Risks, and Comprehensive Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testosterone: Risks and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Chronic Illnesses and Low Testosterone: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Economic Burden of Low Testosterone on American Men's Health and Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Mood Disorders: Impacts and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Weight Loss Boosts Testosterone: Strategies for American Males with Low T [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Diabetes: Interlinked Challenges and Management Strategies for Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Effects on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Osteoporosis: Risks, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Boosting Testosterone in American Men: The Power of Physical Activity and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Prostate Health: Understanding Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hair Loss: Mechanisms and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone: Symptoms, Impact, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Testosterone: What American Men Need to Know and Manage [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Sleep Apnea's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on American Males' Body Composition and Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Heart Disease Risk in American Men: Current Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain and Low Testosterone: A Critical Health Issue for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Low Testosterone: Benefits and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Environmental Estrogens and Declining Testosterone in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Emotional Wellbeing in American Men: Insights and Guidance [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Dietary Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Insights and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Zinc's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Male Libido: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Low Levels [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Depression in American Men: Links, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Metabolic Syndrome: Risks and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Low Testosterone Among American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Thyroid Disorders: Exploring Risks and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Anemia: Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on American Men's Testosterone Levels and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Liver Health and Testosterone: Vital Connections and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalance and Low Testosterone: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Low Testosterone: Impacts and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Respiratory Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Insulin Resistance: A Growing Concern for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Autoimmune Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutritional Deficiencies Impacting Testosterone Levels in American Males: Zinc, Vitamin D, Magnesium [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Neurological Disorders in American Men: Research and Implications [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Gut Microbiome's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Dental Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Emerging Insights [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Dermatological Issues in American Men: Research and Management [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Eye Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Reproductive Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Men: Interventions and Insights [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- ENT Health and Testosterone: Managing Conditions to Boost Hormonal Balance in Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Urological Health: Risks, Detection, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Higher Infection Risk in American Men: Research Insights [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Low Testosterone: A Holistic Endocrine Approach [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Immune System's Role in Testosterone Levels: Impacts and Interventions for American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Psychiatric Risks in American Men: Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Surgical Risks in American Men: Implications and Recommendations [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Trauma's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Clinical Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Rheumatological Conditions and Low Testosterone: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Cancer's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]