Introduction to Late-Onset Hypogonadism
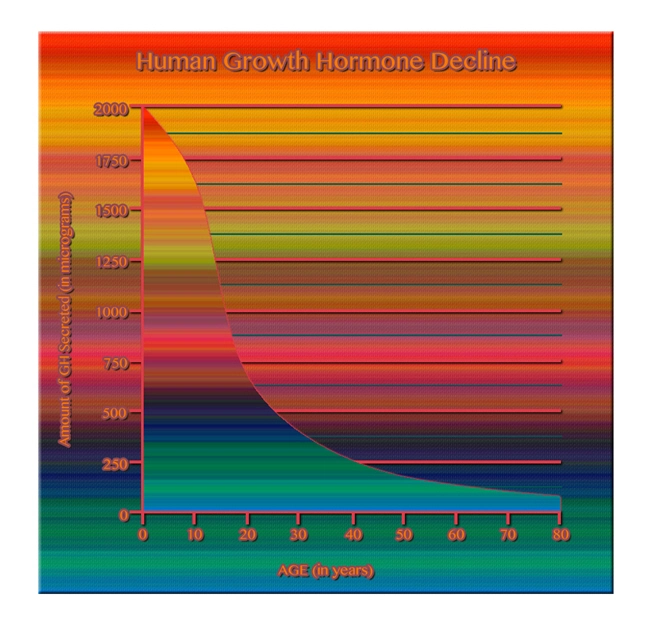
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), commonly referred to as age-related low testosterone, is a clinical and biochemical syndrome characterized by a deficiency in serum testosterone levels in conjunction with associated symptoms. These symptoms can include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, depression, and reduced muscle mass. As American men age, the prevalence of LOH increases, making it a significant health concern that warrants attention and effective management strategies.
The Role of Nutrition in Hormone Regulation
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in the regulation of hormones, including testosterone. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support the body's natural hormone production and help mitigate the symptoms of LOH. Key nutrients that are particularly beneficial include zinc, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Zinc is crucial for testosterone production and is found in foods such as oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds. Vitamin D, which can be obtained from sunlight exposure and fortified foods, has been linked to testosterone levels, with deficiencies associated with lower hormone levels. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and in flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that can support overall hormonal health.
Dietary Strategies to Boost Testosterone
Incorporating specific dietary strategies can help American men manage LOH effectively. A diet that emphasizes whole foods and minimizes processed items can contribute to overall health and hormone balance. For instance, consuming lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables can provide the necessary nutrients to support testosterone production.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as obesity is a known risk factor for LOH. A diet that supports weight management, such as one that is high in fiber and low in sugars, can be beneficial. Intermittent fasting has also been studied for its potential to improve testosterone levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing body fat.
Supplements and Their Efficacy
While a well-rounded diet is the cornerstone of managing LOH, supplements can play a supportive role. Supplements such as zinc, vitamin D, and D-aspartic acid have been studied for their potential to increase testosterone levels. However, it is essential for American men to consult with healthcare providers before starting any supplement regimen, as individual needs and responses can vary.
Lifestyle Factors and Nutrition
Nutrition is not the sole factor in managing LOH; lifestyle choices also play a significant role. Regular physical activity, particularly resistance training, can stimulate testosterone production. Combining exercise with a nutritious diet can create a synergistic effect, enhancing the body's ability to maintain healthy hormone levels.
Moreover, managing stress through techniques such as meditation or yoga can help, as chronic stress can negatively impact testosterone levels. Ensuring adequate sleep is also vital, as sleep deprivation has been linked to lower testosterone.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Managing LOH
For American men facing the challenges of late-onset hypogonadism, a holistic approach that includes a focus on nutrition can be highly effective. By understanding the role of key nutrients and adopting a diet that supports hormone health, men can take proactive steps to manage LOH. Coupled with lifestyle adjustments, such as regular exercise and stress management, nutrition can be a powerful tool in maintaining vitality and well-being as men age. As always, working closely with healthcare professionals to tailor a management plan is recommended to achieve the best outcomes.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging U.S. Men: Challenges and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments and Future Directions for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Men Over 40: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Screening, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mood, Energy, and Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Vitality Maintenance [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevalence, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Holistic Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Long-term Effects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism on American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Life Quality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cognitive Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Independence for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Treatments and Managing Side Effects [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Stress and Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Late-Onset Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Journey and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Careers and Workplace Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Men's Health and Intimate Relationships in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Education, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Risks and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Impacts and Financial Challenges for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cultural Impacts on American Men's Health and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Detection, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Care in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Technological Advances in Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Vital Role of Family Support in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Diagnosis and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Vital Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Self-Esteem: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Peer Support and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Social Impacts and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress Reduction Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Advocacy's Role in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism Through Diet and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for American Men's Mental Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Exercise and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]