Introduction
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), also known as age-related low testosterone, is a clinical and biochemical syndrome characterized by a deficiency in serum testosterone levels in conjunction with specific signs and symptoms. This condition has been increasingly recognized as a significant health concern among aging American males. Concurrently, diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder, affects a substantial portion of the male population in the United States. Recent research has begun to explore the intricate relationship between LOH and diabetes, shedding light on potential shared pathways and clinical implications.
Prevalence and Impact of Late-Onset Hypogonadism
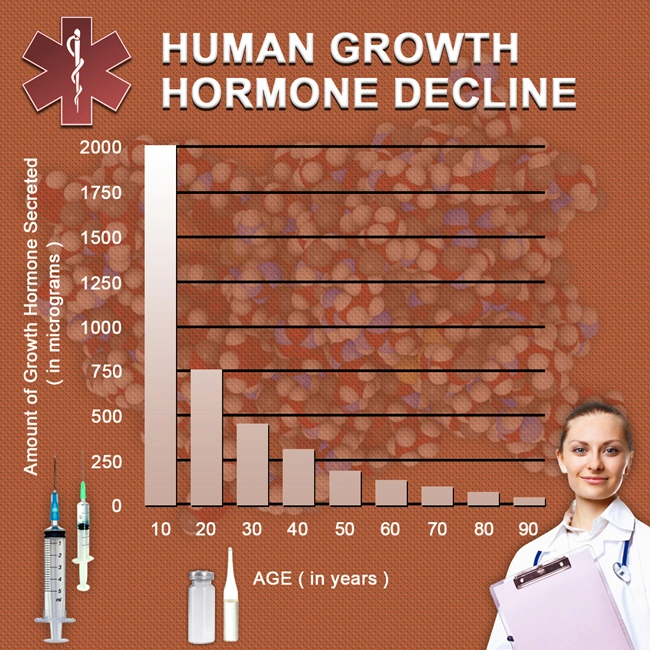
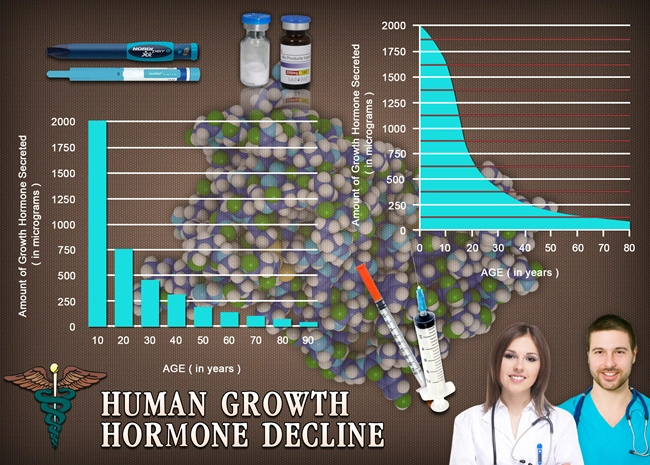
Late-onset hypogonadism is prevalent among American men, with estimates suggesting that up to 39% of men over the age of 45 may experience this condition. Symptoms of LOH include reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and mood disturbances. These symptoms not only diminish quality of life but also contribute to a higher risk of developing other health conditions, including metabolic disorders like diabetes.
Diabetes in American Males
Diabetes is a major health issue in the United States, with approximately 13% of American men diagnosed with the disease. The condition is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to inadequate insulin production or ineffective insulin utilization. Diabetes is associated with numerous complications, including cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and nephropathy, significantly impacting morbidity and mortality rates.
The Interconnection Between LOH and Diabetes
Emerging evidence suggests a bidirectional relationship between LOH and diabetes. Men with LOH are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, while diabetic men are more likely to exhibit symptoms of hypogonadism. This association is thought to be mediated through several mechanisms. Firstly, low testosterone levels can lead to insulin resistance, a key factor in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Secondly, the chronic inflammation and oxidative stress associated with diabetes may impair testosterone production and function.
Clinical Implications and Management
Understanding the link between LOH and diabetes is crucial for the effective management of both conditions. For men with LOH, regular screening for diabetes and other metabolic disorders is recommended. Conversely, diabetic men should be evaluated for signs of hypogonadism, as testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) may offer benefits in managing both conditions. TRT has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce body fat, and enhance overall metabolic health in diabetic men with LOH.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing LOH and diabetes can be challenging due to overlapping symptoms and the need for accurate biochemical assessments. Testosterone levels can fluctuate throughout the day, necessitating multiple measurements for a reliable diagnosis. Similarly, diabetes diagnosis requires careful monitoring of blood glucose levels and consideration of other risk factors. Treatment strategies must be individualized, taking into account the patient's overall health status and potential side effects of therapies.
Future Directions in Research
Further research is needed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the connection between LOH and diabetes. Longitudinal studies could provide insights into the progression of these conditions and the impact of early interventions. Additionally, exploring the role of lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, in managing both LOH and diabetes could offer new avenues for prevention and treatment.
Conclusion
The relationship between late-onset hypogonadism and diabetes in American males represents a critical area of clinical focus. By recognizing the shared pathways and clinical implications of these conditions, healthcare providers can develop more effective strategies for diagnosis and management. As research continues to advance, the hope is to improve the quality of life and health outcomes for affected men across the United States.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging U.S. Men: Challenges and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments and Future Directions for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Men Over 40: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Screening, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mood, Energy, and Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Vitality Maintenance [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Nutrition, Diet, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevalence, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Holistic Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Long-term Effects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism on American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Life Quality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cognitive Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Independence for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Treatments and Managing Side Effects [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Stress and Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Late-Onset Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Journey and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Careers and Workplace Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Men's Health and Intimate Relationships in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Education, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Risks and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Health Impacts and Financial Challenges for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Cultural Impacts on American Men's Health and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Detection, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Care in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Technological Advances in Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Vital Role of Family Support in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Diagnosis and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Vital Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Self-Esteem: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Peer Support and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Social Impacts and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress Reduction Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Advocacy's Role in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism Through Diet and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for American Men's Mental Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Aging Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Exercise and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Impact and Support Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]