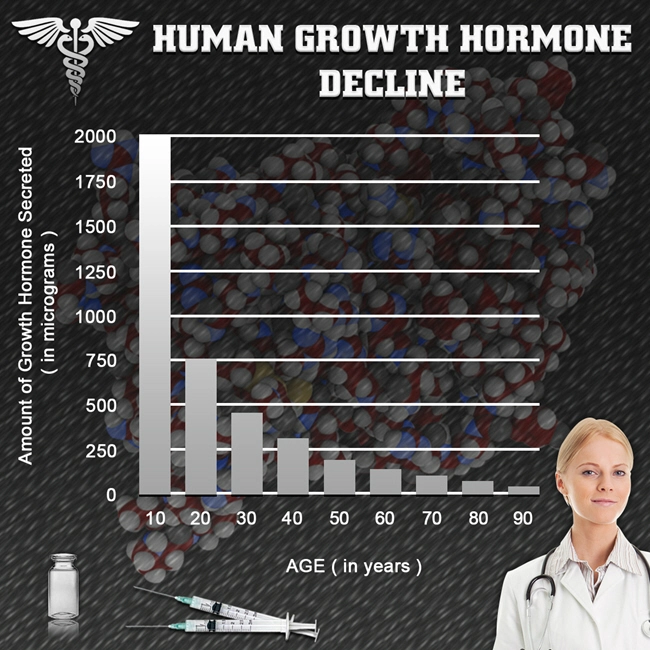
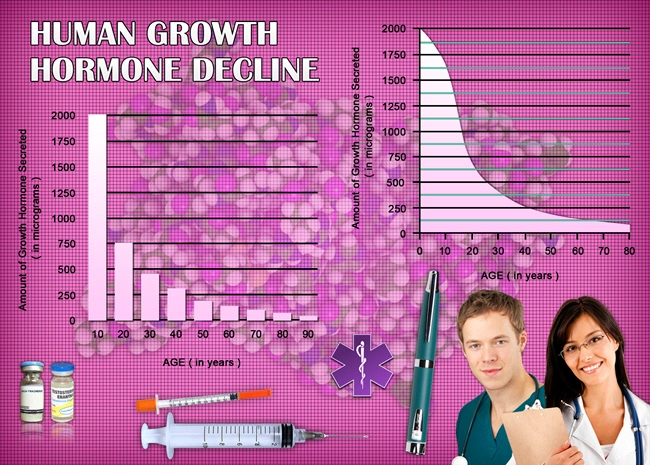
Introduction
Impotence, also known as erectile dysfunction (ED), is a prevalent concern among American males, affecting millions of individuals across various age groups. While numerous factors contribute to this condition, one often overlooked cause is the side effects of medications commonly prescribed for other health issues. This article delves into the intricate relationship between certain drugs and impotence, shedding light on the mechanisms behind this unintended consequence and offering guidance for affected individuals.
Understanding Medication-Induced Impotence
Medication-induced impotence occurs when drugs prescribed for various medical conditions inadvertently interfere with the complex physiological processes involved in achieving and maintaining an erection. The medications most commonly associated with this side effect include antihypertensives, antidepressants, and certain hormonal treatments. These drugs can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters, blood flow, and hormonal regulation necessary for normal erectile function.
Antihypertensive Medications and Impotence
Antihypertensive drugs, used to manage high blood pressure, are among the most frequently implicated in medication-induced impotence. Beta-blockers, such as propranolol and atenolol, can interfere with the sympathetic nervous system's role in initiating an erection. Similarly, diuretics like hydrochlorothiazide may lead to hypokalemia, which can contribute to ED. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and calcium channel blockers have also been associated with impotence, although to a lesser extent.
Antidepressants and Sexual Dysfunction
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), a class of antidepressants widely prescribed for mental health conditions, are notorious for their potential to cause sexual side effects, including impotence. These medications increase serotonin levels in the brain, which can lead to a decrease in sexual desire and difficulty achieving an erection. Other antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), may also contribute to ED in some individuals.
Hormonal Treatments and Their Impact
Certain hormonal treatments, particularly those used in the management of prostate cancer, can have a significant impact on erectile function. Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which reduces testosterone levels, is a common treatment for advanced prostate cancer but is associated with a high incidence of impotence. Additionally, medications used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), such as 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, can also contribute to ED by affecting hormone levels and blood flow to the penis.
Navigating the Challenges of Medication-Induced Impotence
For American males experiencing impotence as a side effect of their medications, it is crucial to engage in open communication with their healthcare providers. Discussing the issue candidly can lead to potential solutions, such as adjusting the dosage, switching to an alternative medication with a lower risk of impotence, or incorporating additional treatments to mitigate the side effects. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management techniques, may also help alleviate the symptoms of medication-induced impotence.
Exploring Treatment Options
When medication-induced impotence persists despite adjustments to the treatment regimen, various therapeutic options are available. Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, such as sildenafil and tadalafil, are commonly prescribed to improve erectile function. These medications work by enhancing blood flow to the penis, helping to counteract the effects of certain drugs. In cases where PDE5 inhibitors are ineffective or contraindicated, other treatments like vacuum erection devices, penile injections, or even surgical implants may be considered.
Conclusion
Medication-induced impotence is a significant concern for many American males, often catching them off guard as they navigate the complexities of managing their health. By understanding the potential side effects of commonly prescribed drugs and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, affected individuals can work towards finding effective solutions. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of medication-induced impotence, it is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals to remain vigilant and proactive in addressing this challenging aspect of men's health.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Revolutionizing Intimacy: Advanced Therapies for Erectile Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 19th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Spectrum of Alternative Therapies for Managing Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 19th, 2025]
- Demystifying the Shadows: A Comprehensive Examination of Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Fractured Masculinity: Overcoming Impotence and Embracing Emotional Freedom [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Behind the Silence: Revealing the Covert Battle Against Male Impotence [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Decoding the Mysteries of Erectile Dysfunction: A Scientific Approach [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Revamping Masculinity: Thriving in Life Despite Male Impotence [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Decoding the Enigma: Unraveling Fallacies and Unveiling Realities about Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Persistence of Potency: Unraveling the Psychological Aftermath of Impotence [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Exploring the Psychological and Societal Impact of Erectile Dysfunction: Addressing Stigma, Treatment Options, and Lifestyle Changes [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Erectile Dysfunction: Early Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Men [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring Testosterone's Impact on Male Sexual Health and Impotence Management [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Stress and Erectile Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Navigating Impotence in Relationships: Communication Strategies and Maintaining Intimacy Together [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Male Impotence: A Path to Recovery and Success Stories [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Emotional and Relational Impact of Impotence: Navigating Challenges for Stronger Relationships [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments Revolutionizing Impotence Care in American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Male Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Overcoming Impotence Through Lifestyle Changes [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Understanding the Therapeutic Pathway: Emotional Recovery from Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Impotence: Understanding, Managing, and Rebuilding Intimacy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Diabetes and Impotence in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- American Men's Triumph Over Impotence: Breaking Silence and Stigma [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: Breaking Stigma, Seeking Help, and Empowering Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Restorative Sleep: Key to Enhancing Sexual Health and Managing Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Impotence: Causes, Treatments, and Empowerment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Telemedicine Revolutionizes Impotence Care for American Men: Benefits and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Impotence in Aging Men: Biological, Psychological, and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Mental Resilience: Key to Overcoming Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Economic and Emotional Toll of Impotence on American Men: A Holistic View [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Impotence in American Males: Causes, Treatments, and Triumphs [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Exploring Aphrodisiacs for Impotence: Scientific Insights and Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Causes, Treatments, and Restoring Intimacy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Global Perspectives on Impotence: Cultural Views and Treatments for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Work Stress and Impotence: Understanding Links and Managing Effects in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Redefining Sexual Success: Understanding and Overcoming Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Essential Vitamins and Minerals to Combat Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Obesity, Diet, and Impotence: A Guide for American Males' Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Debunking Impotence Myths: Empowering American Men with Facts and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Erectile Dysfunction: Breaking the Silence and Stigma [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exploring Secondary Causes of Impotence in American Men Beyond Medication [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Smoking, Alcohol, and Impotence: Risks and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- PDE5 Inhibitors: Revolutionizing Erectile Dysfunction Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Innovative Approaches Revolutionizing Impotence Treatment and Diagnosis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Innovative Gadgets and Therapies Revolutionize ED Treatment and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: Strategies for Enhancing Seduction and Intimacy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Choices Impacting Male Sexual Health: Diet, Exercise, and More [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Impotence: Understanding Links and Managing Effects [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Acupuncture as a Complementary Therapy for Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: Partners' Role in Recovery and Intimacy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Impotence and Self-Esteem: Counseling Strategies for Recovery and Resilience [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Causes, Treatments, and Holistic Recovery Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Impotence: Anatomy, Blood Flow, and Holistic Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy: A Comprehensive Approach to Treating Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Impotence: Hormonal Imbalances and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Psychological Approaches to Managing and Overcoming Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Potent Remedy for Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: Understanding Causes and Embracing Sexual Wellness in Modern Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Effective Erectile Dysfunction Treatment in the US [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Psychological Impacts and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Evolving Treatments for Impotence: From Ancient Remedies to Future Innovations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Impotence: Unveiling Emotional, Financial Burdens and Seeking Supportive Solutions [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Innovative Devices and Technologies Revolutionizing Impotence Treatment [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Exploring Injection and Device Therapies for Effective ED Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Emotional Challenges of Impotence: Coping Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Redefining Masculinity and Seeking Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Impotence and Mental Health: Understanding Links and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: American Men's Journeys to Recovery and Confidence [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Complementary Approaches to Managing Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Understanding Impotence: Biochemical, Hormonal, and Psychological Factors in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Surgical Options for Impotence: Types, Considerations, and Outcomes [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Impotence Treatment Advances: Personalized, Non-Invasive Options on the Horizon [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Psychological Impacts and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Prostate Health and Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Chronic Illness and Impotence: Understanding Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins and Male Sexual Health: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Hacks to Combat Impotence: Diet, Exercise, and More for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Understanding, Breaking Stigma, and Seeking Treatment [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Impotence Treatment: Gene Therapy, Stem Cells, and New Drugs [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Impotence: Insights into ED Predisposition Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]