Introduction to Hypopituitarism and PCOS
Hypopituitarism and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are two distinct endocrine disorders that significantly impact women's health. Hypopituitarism is characterized by the decreased secretion of one or more of the eight hormones produced by the pituitary gland, a small but crucial organ at the base of the brain. On the other hand, PCOS is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age, marked by enlarged ovaries containing numerous small cysts. Both conditions can lead to a myriad of health issues, ranging from fertility problems to metabolic disturbances.
The Pathophysiology of Hypopituitarism
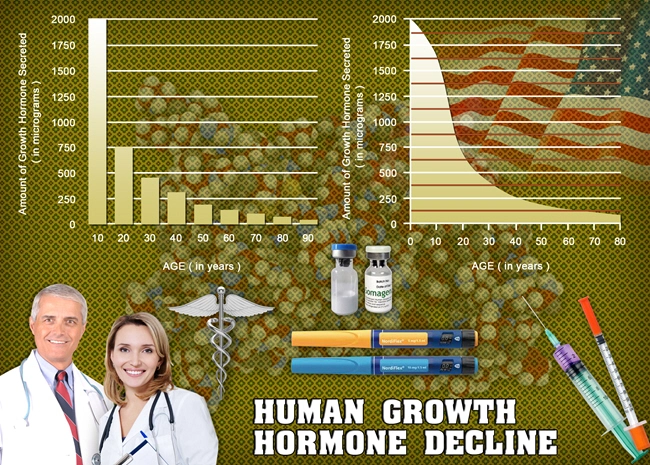
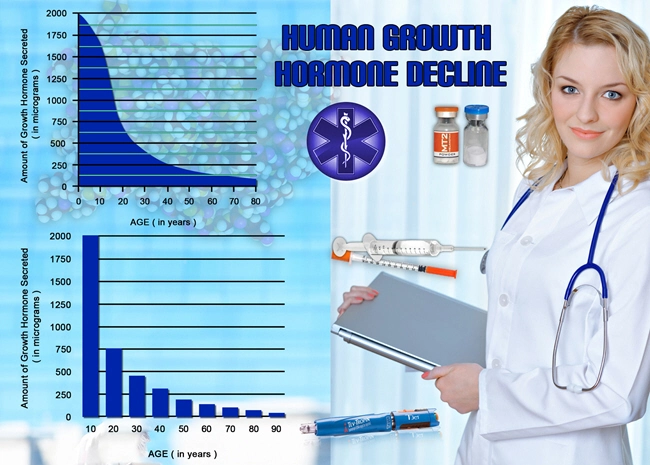
Hypopituitarism can arise from various causes, including tumors, head injuries, radiation therapy, or autoimmune conditions. The deficiency in pituitary hormones can disrupt the normal functioning of the thyroid, adrenal glands, and gonads, leading to a broad spectrum of symptoms. These may include fatigue, weakness, weight changes, and sexual dysfunction. In women, hypopituitarism can lead to irregular menstrual cycles or amenorrhea, which can further complicate fertility and overall health.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
PCOS is a multifaceted disorder with a strong genetic component, often manifesting in irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. The exact cause of PCOS remains elusive, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Women with PCOS are at an increased risk of developing insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can also lead to hirsutism, acne, and alopecia, significantly affecting the quality of life.
The Interplay Between Hypopituitarism and PCOS
While hypopituitarism and PCOS are separate conditions, they can intersect in complex ways. For instance, hypopituitarism can lead to secondary amenorrhea, which might be misdiagnosed as PCOS due to similar symptoms such as irregular periods. Conversely, the hormonal imbalances in PCOS can sometimes mask the symptoms of hypopituitarism, complicating diagnosis and treatment. It is crucial for healthcare providers to conduct thorough evaluations to differentiate between these conditions and tailor treatment accordingly.
Diagnostic Challenges and Strategies
Diagnosing hypopituitarism and PCOS can be challenging due to their overlapping symptoms and the need for specialized testing. For hypopituitarism, hormone level assessments and imaging studies like MRI are essential to identify pituitary abnormalities. PCOS diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, ultrasound imaging of the ovaries, and blood tests to measure hormone levels. Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective management and to prevent long-term health complications.
Management and Treatment Approaches
The management of hypopituitarism involves hormone replacement therapy to restore deficient hormones and alleviate symptoms. This may include thyroid hormone, cortisol, and sex hormone replacements, tailored to the individual's needs. For PCOS, treatment often focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This can include lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, to address insulin resistance, and medications like oral contraceptives to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels.
Long-term Health Implications
Both hypopituitarism and PCOS have significant long-term health implications. Women with hypopituitarism may face increased risks of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and mental health issues if not properly managed. Similarly, women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing metabolic syndrome, which can lead to diabetes and heart disease. Regular monitoring and comprehensive care are essential to mitigate these risks and improve quality of life.
Conclusion: A Call for Integrated Care
The complexities of hypopituitarism and PCOS underscore the need for integrated care approaches. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in recognizing the signs of these conditions and adept at differentiating between them. Collaborative efforts between endocrinologists, gynecologists, and other specialists can enhance patient outcomes. By fostering a deeper understanding of these disorders and their impacts on women's health, we can pave the way for more effective treatments and improved quality of life for affected individuals.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Hypopituitarism and Cardiovascular Health: Unraveling the Intricate Links in American Males [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Metabolic Syndrome in American Males: An Emerging Health Crisis [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- American Males' Experiences with Hypopituitarism: Challenges and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Cardiovascular Risks: Hypopituitarism and Heart Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Connection: Hypopituitarism and Uterine Fibroids in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypopituitarism and Its Impact on Male Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Hormonal Nexus: Hypopituitarism and Its Implications for Breast Cancer in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Autoimmune Disorders: Insights and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Cognitive Impact on American Males: Memory, Attention, and Executive Function [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Obesity in American Males: Hormonal Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Sleep in American Men: Hormonal Imbalances and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in Aging American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Cancer Risk in American Males: Monitoring and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Tumors: Surgical Treatment and Outcomes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impacts and Management of Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Multidisciplinary Care Essential for Managing Hypopituitarism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Impact on Skin Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Anemia in American Males: The Role of Erythropoietin Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Imbalances and Joint Health Impacts [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hearing Loss: Exploring Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and CFS Overlap: Implications for American Males' Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Migraines in American Males: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Liver Health in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impacts on Eye Health and Vision [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Asthma in American Males: Hormonal Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Role in Alzheimer's: Hormonal Imbalances and Cognitive Decline [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hair Loss in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Emerging Treatments [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Osteoarthritis in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Lupus Link in American Males: Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and CKD: Pathophysiology, Monitoring, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impacts on Immune System and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gout Link: Uric Acid's Role in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gallbladder Disease: Exploring Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Liver Cirrhosis: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Sjögren's Syndrome: Impacts on Exocrine Glands in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Hypopituitarism and MS Connection in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Parkinson's: Neurodegenerative Impacts on American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Heart Disease Risks in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Pancreatitis: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Allergies in American Men: Exploring Hormonal and Immune Links [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Stroke Risk and Hormonal Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Fibromyalgia: Overlapping Symptoms and Diagnostic Challenges in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Seizures: Neurological Links and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hypertension: Impacts on Blood Pressure in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Link to Ovarian Cancer: Implications for American Male Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Link Between Hypopituitarism and RA in American Males: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Prostate Cancer: Understanding and Managing the Interplay in Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and IBD in American Males: Clinical Insights and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Diabetes Mellitus: Impacts on Glucose Metabolism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Lipid Disorders in American Males: Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders in American Males: Hypopituitarism and Adrenal Cancer Link Explored [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Link Between Hypopituitarism and Celiac Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Breast Cancer Link in American Males: Hormonal Insights and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Cancer: Impact, Detection, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances Linking Hypopituitarism and Thyroid Cancer in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Benign Tumors in American Males: Exploring Gynecological Links [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Testicular Cancer: Impacts on Male Fertility and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hormonal Links Between Hypopituitarism and Endometriosis in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism: Impact on Female Reproductive and Vaginal Health Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Male Sexual Health and Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Premature Ejaculation: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies in American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Penile Health and Male Reproductive Function [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Exploring Metabolic Links: Hypopituitarism and Gestational Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in Males: Exploring Links to Miscarriage and Fertility Issues [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Cervical Cancer: Hormonal Monitoring in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Lactation in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Postpartum Depression: Impacts on Mental Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Preeclampsia: The Critical Role of Hormonal Monitoring in Pregnancy [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Ectopic Pregnancy: Impacts and Management in Women's Health [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Male Fertility: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impact on Acne and Skin Health Management [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Alopecia in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Understanding Vision Loss and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Andropause: Impacts and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Vestibular Dysfunction: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hirsutism in American Males: Hormonal Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]