Introduction
Hypopituitarism and Multiple Sclerosis (MS) are two distinct medical conditions that can significantly impact the quality of life of American males. While hypopituitarism involves the underproduction of hormones by the pituitary gland, MS is an autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system. Recent research has begun to explore a potential connection between these two conditions, raising questions about shared pathophysiological mechanisms and the implications for diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Hypopituitarism
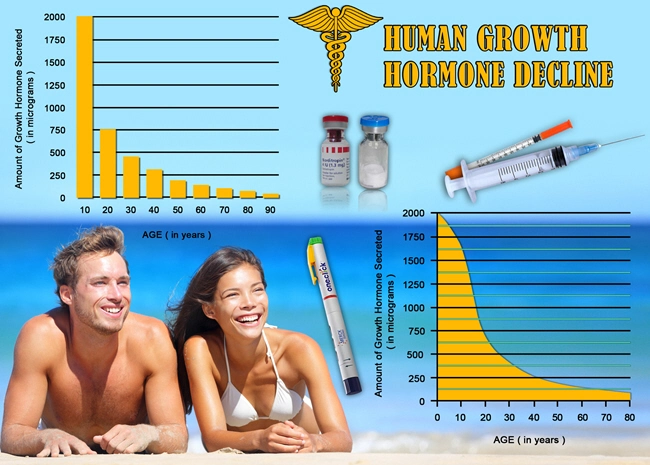
Hypopituitarism is characterized by the inadequate secretion of one or more pituitary hormones, which can lead to a cascade of hormonal imbalances throughout the body. Common symptoms in American males may include fatigue, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and muscle weakness. The condition can result from various causes, such as tumors, traumatic brain injury, or radiation therapy. Early diagnosis and hormone replacement therapy are crucial for managing hypopituitarism and improving patients' quality of life.
Exploring Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This demyelination can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including muscle weakness, numbness, vision problems, and cognitive impairment. In American males, MS can manifest differently than in females, with some studies suggesting a higher prevalence of progressive forms of the disease. Treatment typically involves disease-modifying therapies to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses, along with symptomatic management.
Investigating the Potential Connection
Recent studies have begun to investigate a possible link between hypopituitarism and MS. One theory suggests that the pituitary gland's dysfunction could contribute to the immune system's dysregulation, potentially increasing the risk of developing autoimmune diseases like MS. Additionally, some research has found a higher prevalence of pituitary abnormalities in patients with MS compared to the general population.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that a significant proportion of MS patients exhibited hypopituitarism, particularly those with a longer disease duration. The authors hypothesized that chronic inflammation and the use of certain MS medications might contribute to pituitary dysfunction. However, more research is needed to establish a causal relationship and understand the underlying mechanisms.
Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment
The potential connection between hypopituitarism and MS has important implications for the diagnosis and management of both conditions in American males. Clinicians should be aware of the possibility of co-occurrence and consider screening for hypopituitarism in MS patients, especially those with symptoms suggestive of hormonal imbalances. Similarly, patients with hypopituitarism should be monitored for signs of neurological dysfunction that could indicate the development of MS.
In terms of treatment, the management of hypopituitarism in MS patients may require a more nuanced approach. Hormone replacement therapy must be carefully titrated to avoid exacerbating MS symptoms or interfering with disease-modifying therapies. Collaborative care between endocrinologists and neurologists is essential to optimize outcomes for patients with both conditions.
Future Research Directions
As the potential link between hypopituitarism and MS continues to be explored, several areas of future research are warranted. Longitudinal studies are needed to assess the incidence and prevalence of hypopituitarism in MS patients over time. Additionally, investigations into the specific mechanisms by which pituitary dysfunction may contribute to the development or progression of MS could lead to novel therapeutic targets.
Furthermore, research focused on American males is crucial, given the potential sex-specific differences in the presentation and progression of both hypopituitarism and MS. Understanding these differences could inform more personalized approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
The emerging evidence of a potential connection between hypopituitarism and Multiple Sclerosis in American males highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to these complex conditions. By recognizing the possibility of co-occurrence and tailoring management strategies accordingly, healthcare providers can improve outcomes for patients. As research in this field continues to evolve, it is hoped that a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms will lead to more effective treatments and ultimately, a better quality of life for those affected by these challenging disorders.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Hypopituitarism and Cardiovascular Health: Unraveling the Intricate Links in American Males [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Metabolic Syndrome in American Males: An Emerging Health Crisis [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- American Males' Experiences with Hypopituitarism: Challenges and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Cardiovascular Risks: Hypopituitarism and Heart Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Connection: Hypopituitarism and Uterine Fibroids in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypopituitarism and Its Impact on Male Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Hormonal Nexus: Hypopituitarism and Its Implications for Breast Cancer in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Autoimmune Disorders: Insights and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Cognitive Impact on American Males: Memory, Attention, and Executive Function [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Obesity in American Males: Hormonal Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Sleep in American Men: Hormonal Imbalances and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in Aging American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Cancer Risk in American Males: Monitoring and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Tumors: Surgical Treatment and Outcomes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impacts and Management of Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Multidisciplinary Care Essential for Managing Hypopituitarism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Impact on Skin Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Anemia in American Males: The Role of Erythropoietin Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Imbalances and Joint Health Impacts [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hearing Loss: Exploring Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and CFS Overlap: Implications for American Males' Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Migraines in American Males: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Liver Health in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impacts on Eye Health and Vision [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Asthma in American Males: Hormonal Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Role in Alzheimer's: Hormonal Imbalances and Cognitive Decline [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hair Loss in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Emerging Treatments [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Osteoarthritis in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Lupus Link in American Males: Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and CKD: Pathophysiology, Monitoring, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impacts on Immune System and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gout Link: Uric Acid's Role in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gallbladder Disease: Exploring Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Liver Cirrhosis: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Sjögren's Syndrome: Impacts on Exocrine Glands in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Parkinson's: Neurodegenerative Impacts on American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Heart Disease Risks in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Pancreatitis: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Allergies in American Men: Exploring Hormonal and Immune Links [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Stroke Risk and Hormonal Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Fibromyalgia: Overlapping Symptoms and Diagnostic Challenges in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Seizures: Neurological Links and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hypertension: Impacts on Blood Pressure in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Link to Ovarian Cancer: Implications for American Male Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Link Between Hypopituitarism and RA in American Males: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Prostate Cancer: Understanding and Managing the Interplay in Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and IBD in American Males: Clinical Insights and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Diabetes Mellitus: Impacts on Glucose Metabolism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Lipid Disorders in American Males: Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders in American Males: Hypopituitarism and Adrenal Cancer Link Explored [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Link Between Hypopituitarism and Celiac Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Breast Cancer Link in American Males: Hormonal Insights and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Cancer: Impact, Detection, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances Linking Hypopituitarism and Thyroid Cancer in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Benign Tumors in American Males: Exploring Gynecological Links [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Testicular Cancer: Impacts on Male Fertility and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hormonal Links Between Hypopituitarism and Endometriosis in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism: Impact on Female Reproductive and Vaginal Health Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and PCOS: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Integrated Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Male Sexual Health and Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Premature Ejaculation: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies in American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Penile Health and Male Reproductive Function [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Exploring Metabolic Links: Hypopituitarism and Gestational Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in Males: Exploring Links to Miscarriage and Fertility Issues [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Cervical Cancer: Hormonal Monitoring in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Lactation in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Postpartum Depression: Impacts on Mental Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Preeclampsia: The Critical Role of Hormonal Monitoring in Pregnancy [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Ectopic Pregnancy: Impacts and Management in Women's Health [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Male Fertility: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impact on Acne and Skin Health Management [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Alopecia in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Andropause: Impacts and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hirsutism in American Males: Hormonal Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Menopause: Hormonal Imbalances and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]