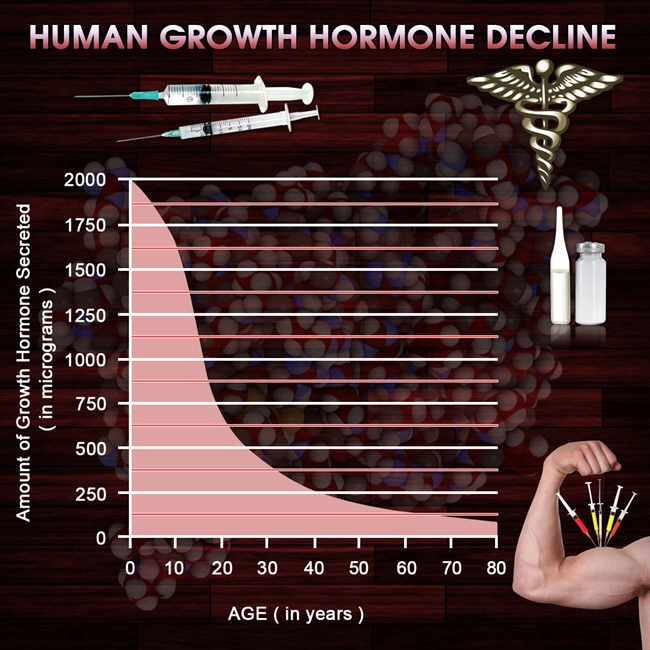
Introduction to Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, presents a significant challenge in men's health. This hormonal imbalance can lead to a myriad of symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, and mood disturbances, significantly impacting the quality of life. In the realm of primary care, where the initial diagnosis and management often occur, it is imperative to adhere to established medical guidelines to ensure the best outcomes for patients.
Diagnosis of Hypogonadism
The diagnosis of hypogonadism begins with a thorough clinical evaluation. Primary care physicians should be vigilant for symptoms such as reduced sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and decreased muscle mass. Laboratory testing is crucial, with total testosterone levels being the primary biomarker. According to the Endocrine Society, a morning serum testosterone level below 300 ng/dL on two separate occasions warrants further investigation. Additionally, assessing luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels can help distinguish between primary and secondary hypogonadism.
Treatment Strategies
Once hypogonadism is confirmed, treatment should be tailored to the individual's needs. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is the cornerstone of management for most patients. Available formulations include intramuscular injections, transdermal patches, gels, and buccal tablets. Each method has its advantages and potential side effects, and the choice should be made in collaboration with the patient, considering lifestyle and preferences.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Monitoring is a critical component of hypogonadism management. After initiating TRT, patients should be reassessed at three months to evaluate symptom improvement and monitor for adverse effects. Key parameters to monitor include hematocrit levels, as testosterone can increase red blood cell production, potentially leading to polycythemia. Additionally, bone mineral density, lipid profiles, and prostate health should be regularly assessed to ensure the therapy's safety and efficacy.
Special Considerations
In managing hypogonadism, special attention must be paid to certain populations. Older men and those with pre-existing cardiovascular disease require a more cautious approach to TRT. The potential risks, including cardiovascular events and prostate cancer, must be weighed against the benefits. Furthermore, fertility preservation is a crucial consideration for younger men, as TRT can suppress spermatogenesis. In such cases, alternative treatments like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) may be considered.
Patient Education and Lifestyle Modifications
Empowering patients through education is fundamental in the management of hypogonadism. Patients should be informed about the importance of adherence to therapy and the potential side effects. Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can also play a significant role in improving symptoms and overall well-being. Encouraging patients to engage in these healthy behaviors can enhance the effectiveness of TRT and contribute to better health outcomes.
Conclusion
The management of hypogonadism in primary care requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment, vigilant monitoring, and patient education. By adhering to established medical guidelines and considering the unique needs of each patient, primary care physicians can significantly improve the quality of life for men affected by this condition. As research continues to evolve, staying abreast of the latest developments will ensure that the care provided remains at the forefront of medical science.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 24th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Best Practices in Monitoring Hypogonadism: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Sleep Disorders: A Bidirectional Impact on Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Muscle Health Dilemma: The Role of Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Navigating Hypogonadism in Men with Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Impaired Wound Healing in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Connection Between Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Liver Health: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Medical Education Essentials [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Chronic Pain: Integrated Treatment Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Thyroid Function: Interplay and Impact on Male Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Disorders: Insights and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Ethical Challenges in Diagnosing and Treating Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Prostate Health: Understanding and Managing Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Screening and Management Guidelines for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men: Physical, Mental, and Social Effects [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cancer Risk: Understanding Links and Managing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Medical Imaging's Crucial Role in Diagnosing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Health in American Males: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Health and Therapeutic Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Gastrointestinal Health: A Bidirectional Impact in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Health: Treatments and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism and Kidney Disease in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Innovations in Hypogonadism Treatment: From TRT to Personalized Medicine [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Preventing Hypogonadism in American Males: Strategies and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health and Testosterone Replacement Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Blood Pressure: Understanding Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Medical Rehabilitation for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Headaches: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Monitoring Hypogonadism in Long-Term Care: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Joint Health and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Multidisciplinary Medical Teams [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Neurological Disorders in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact on Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Psychological Counseling Needs for American Males with Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Anemia in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Dental Health: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact: Understanding and Managing Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cholesterol: A Critical Link Impacting Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Promising Approach to Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Trends, Treatments, and Future Research Directions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Understanding Links and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hearing Loss: Exploring the Link and Implications for Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Transgender Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Technology's Role in Diagnosing Hypogonadism: Advances and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Balance: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Allergies: Exploring the Medical Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Eye Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Vision: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism-Related Fatigue: Therapies and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and GERD: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Urinary Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Monitoring Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Medical Social Workers: Vital Support for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Accelerated Skin Aging in American Males: Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Strategies to Enhance Adherence to Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Peripheral Neuropathy in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Nail Health in American Males: Symptoms and Management [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gallbladder Health in American Males: Emerging Links and Insights [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Wound Healing in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Medical Devices Revolutionize Hypogonadism Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Men: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Sinus Health: Testosterone's Role and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Management in American Males with Chronic Illnesses: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Nurses' Crucial Role in Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Spleen Health in American Males: Emerging Links and Implications [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Ear Health: Understanding and Managing in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Medical Counseling: Essential for Effective Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Lymphatic Function in American Males: Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Adrenal Function: Impacts and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Pineal Gland: Emerging Links and Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Medical Dietitians' Role in Managing Hypogonadism Through Nutrition and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Pituitary Health Impact [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Health: Interplay and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Thymus Health and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in American Males with Genetic Disorders: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]