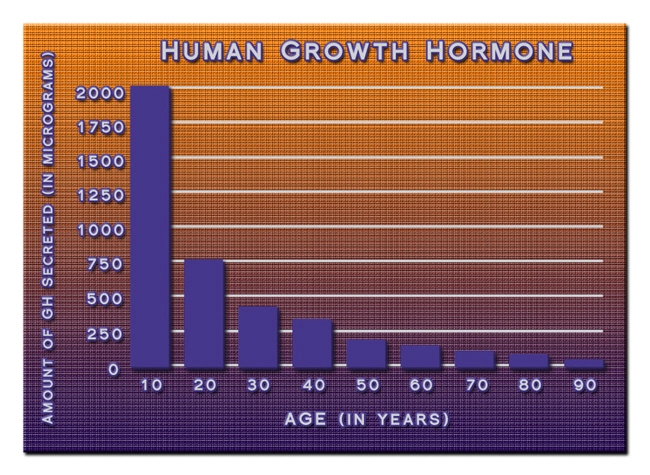
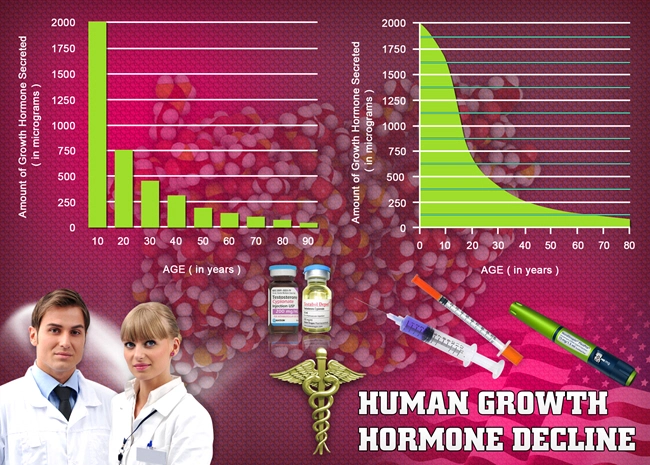
Introduction to Human Growth Hormone
Human Growth Hormone (HGH) is a pivotal peptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland, instrumental in growth, cell repair, and metabolism. In American males, understanding the role of HGH extends beyond its traditional associations with physical development, delving into its influence on vital organ function, particularly the liver.
The Liver's Role in the Body
The liver, a cornerstone of human physiology, is responsible for a myriad of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. For American males, maintaining optimal liver health is crucial for overall well-being and longevity.
HGH and Liver Function
Research has illuminated the intricate relationship between HGH and liver function. HGH stimulates the liver to produce Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1), which plays a significant role in cellular growth and metabolism. This interaction underscores the liver's importance as a mediator of HGH's systemic effects.
Detoxification and HGH
Detoxification, the liver's process of neutralizing and eliminating toxins, is vital for maintaining health. HGH influences this process by enhancing the liver's capacity to metabolize drugs and toxins. Studies have shown that HGH can increase the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are critical for the breakdown of various substances in the liver.
HGH Deficiency and Liver Health
In American males, HGH deficiency can lead to impaired liver function. Reduced levels of HGH may result in decreased production of IGF-1, which can compromise the liver's ability to perform its essential tasks, including detoxification. This can manifest as increased susceptibility to liver disease and a diminished capacity to handle metabolic stress.
Therapeutic Implications of HGH
For American males facing liver-related health challenges, the therapeutic use of HGH presents potential benefits. HGH therapy can enhance liver function by boosting IGF-1 levels, thereby supporting the liver's detoxification processes. However, it is crucial to approach HGH therapy with caution, as improper use can lead to adverse effects.
Considerations for American Males
American males should be aware of the factors that can influence HGH levels, such as age, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions. Regular monitoring of liver function and HGH levels can help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
Conclusion
The relationship between HGH and liver function is a critical aspect of health for American males. By understanding how HGH influences liver detoxification and overall liver health, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal function. As research continues to evolve, the potential for HGH to support liver health offers a promising avenue for enhancing the well-being of American males.
In conclusion, the interplay between HGH and liver function underscores the importance of a holistic approach to health. American males should consider the role of HGH in their overall health strategy, ensuring that they support their liver's vital functions through informed lifestyle choices and, when necessary, appropriate medical interventions.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Maximizing Your Potential: Dietary Strategies to Enhance Human Growth Hormone in American Males [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 24th, 2025]
- Decoding the Biochemical Enigma: Unveiling the Intricacies of Human Growth Hormones [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- The Powerhouse of Biological Growth: Unlocking the Discernments of Human Growth Hormone [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Riddle of Longevity: A Deep Dive into the Anti-Aging Potential of HGH [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Marvel of Human Biology: The Intricate Role of Human Growth Hormone [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Embarking on the Path to Comprehension: Everything You Need to Know about Human Growth Hormone [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Delving Deep: Unraveling the Human Growth Hormone Enigma [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Orchestration in The Body: Harmonizing Roles of HGH with Other Hormones [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Exploring the Multifaceted Impact of Human Growth Hormone on Organ Health: From Cardiovascular to Cognitive Functions [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Expanding Horizons in Growth Hormone Therapy Applications [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Human Growth Hormone: Natural vs. Synthetic Approaches [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring Human Growth Hormone: Benefits for Muscle, Bone, and Skin Health in Men [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Optimizing Human Growth Hormone for Enhanced Fitness Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Guide to HGH Deficiency: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Vital Role of HGH in Men's Health: Muscle, Fat, and Energy Metabolism [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Optimizing HGH Production: The Crucial Role of Sleep Quality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 10th, 2025]
- HGH's Impact on Athletic Performance: Benefits, Risks, and Natural Enhancement for American Males [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Unlocking the Secrets of Youth: The Advancements in HGH Therapy for Anti-Aging [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Unlocking the Power of HGH: Lifestyle Strategies for American Males to Boost Natural Growth Hormone Levels [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Unleashing the Power of Exercise: How Workouts Boost Human Growth Hormone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Legal and Ethical Challenges of Human Growth Hormone Use in Sports and Medicine [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Stress, Cortisol, and HGH: Optimizing Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Human Growth Hormone: Risks, Misuse, and Ethical Concerns in Fitness and Sports [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- HGH's Cellular Impact on American Males: Growth, Muscle, and Health [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- HGH Market Trends, Costs, and Impacts on American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy in Aging Males: Benefits, Risks, and Ethical Considerations [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- HGH's Potential Cardiovascular Benefits for American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy: Enhancing Growth and Health in Children with Disorders [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- HGH's Impact on Immune Health in American Males: Strategies and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- HGH Decline in Aging American Males: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Human Growth Hormone: From Discovery to Clinical Applications and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- HGH's Role in Bone Health for American Males: Growth, Density, and Healing [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- HGH Benefits for American Males: Muscle Gain and Fat Loss Optimization [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Environmental Factors Impacting HGH Production in American Males: Sleep, Diet, Exercise, Toxins, Stress, Age [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Innovative HGH Delivery Systems: Enhancing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Recombinant HGH: Benefits, Applications, and Safety for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- HGH's Comprehensive Impact on Organ Systems in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- HGH's Impact on Recovery and Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- HGH Therapy Advances: Benefits, Research, and Safety for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- HGH's Daily Impact on Energy and Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- HGH's Role in Preventing Osteoporosis in American Males: Current Insights and Future Directions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing HGH Deficiency in American Males: Treatments and Lifestyle Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Debunking HGH Myths: Risks, Benefits, and Realistic Expectations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- High-Intensity Workouts Boost HGH for Muscle Growth and Fat Loss in Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- HGH and IGF-1: Enhancing Male Health, Muscle Growth, and Longevity [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- HGH in Sports: Ethical Dilemmas and Health Risks for American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- HGH and Longevity: Benefits, Risks, and Lifestyle Impact for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- HGH's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males: Growth, Benefits, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Human Growth Hormone: Benefits, Risks, and Aging Gracefully in Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Obesity's Impact on HGH Levels in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Human Growth Hormone: Impacts on Growth, Metabolism, and Aging in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HGH in Regenerative Medicine: Enhancing Vitality and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HGH's Role in Growth, Aging, and Health for American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HGH Synergy with Testosterone, Supplements, Exercise, and Sleep for American Males' Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormonal Optimization: Enhancing HGH for Peak Performance and Vitality in Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HGH Benefits for American Males in Accelerating Wound Healing and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy: Enhancing Health in American Males Through Holistic Integration [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Intermittent Fasting Boosts HGH: Benefits for American Males' Health and Fitness [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy: Enhancing Quality of Life for American Males with Chronic Illnesses [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HGH's Role in Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Acromegaly in American Males: Diagnosis, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HGH's Impact on Skin Health: Collagen, Elastin, and Hydration for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HGH in Women: Benefits, Challenges, and Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy Success in American Men: Case Studies on Health and Performance [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HGH Supplements: Efficacy, Safety, and Natural Alternatives for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Genetic and Familial Influences on HGH Production in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Maximizing HGH Release: Sleep Strategies for American Males' Health Optimization [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- HGH's Role in Cognitive Enhancement: Benefits and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- HGH Benefits for Muscle Recovery and Athletic Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- HGH Testing for American Males: Types, Procedures, and Importance [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- HGH Innovations: Enhancing Health and Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Mindfulness and Meditation Boost HGH Levels in American Men by Reducing Stress [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Optimizing HGH Levels: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Management for American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- HGH's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- HGH in Sports: Ethical Dilemmas, Health Risks, and the American Male Athlete [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- HGH's Role in Tissue Renewal and Health for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy: Benefits, Side Effects, and Long-Term Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy for American Males: Balancing Costs and Health Benefits [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- HGH's Role in Enhancing Immune Function in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- HGH Therapy for American Males: Benefits, Risks, and Lifestyle Considerations [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]