Introduction
Testosterone propionate, a commonly used anabolic steroid, has been a subject of interest in medical research due to its potential impact on various health conditions. Among American males, the prevalence of diabetes has been on the rise, prompting investigations into the possible links between testosterone propionate use and the development of this metabolic disorder. This article delves into the current understanding of the relationship between testosterone propionate and diabetes, providing valuable insights for American men.
Testosterone Propionate: An Overview
Testosterone propionate is a synthetic derivative of testosterone, a hormone naturally produced in the male body. It is often used in medical settings to treat conditions such as hypogonadism, where the body fails to produce sufficient testosterone. However, its use has extended beyond medical purposes, with some individuals using it for performance enhancement or bodybuilding. The potential health implications of its non-medical use have raised concerns among healthcare professionals.
The Diabetes Epidemic Among American Males
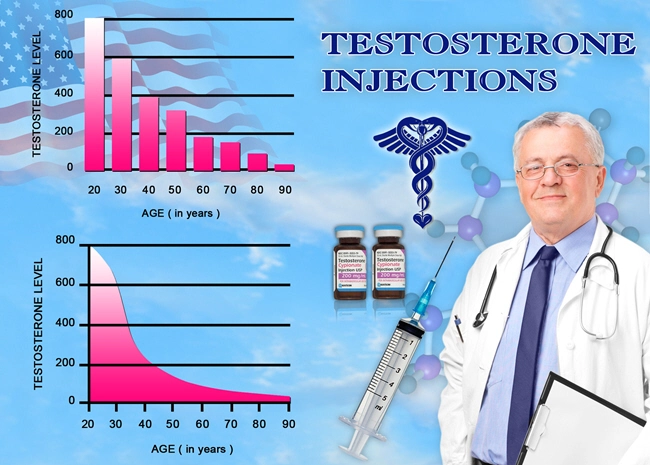
Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, has become a significant public health concern in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 13% of American men aged 18 and older have been diagnosed with diabetes. The condition is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, which can lead to various complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Exploring the Link Between Testosterone Propionate and Diabetes
Recent studies have begun to investigate the potential association between testosterone propionate use and the development of diabetes in American males. One study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that men using testosterone propionate had a higher risk of developing insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. The researchers suggested that the anabolic steroid may disrupt normal glucose metabolism, leading to impaired insulin function.
Another study conducted by the American Diabetes Association explored the impact of testosterone propionate on body composition and metabolic health. The findings indicated that men using the steroid experienced an increase in visceral fat, a type of fat stored around the organs that is strongly linked to insulin resistance and diabetes. The study also noted that testosterone propionate use was associated with decreased insulin sensitivity, further supporting the potential link to diabetes.
Mechanisms Behind the Association
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the potential link between testosterone propionate and diabetes. One theory suggests that the steroid may directly affect insulin signaling pathways, leading to impaired glucose uptake by cells. Another hypothesis is that testosterone propionate may alter lipid metabolism, promoting the accumulation of harmful fats that contribute to insulin resistance.
Additionally, the use of testosterone propionate has been associated with changes in body composition, such as increased muscle mass and decreased fat mass. While these changes may be desirable for some individuals, they can also lead to metabolic imbalances that increase the risk of diabetes.
Implications for American Males
The potential link between testosterone propionate and diabetes has significant implications for American males, particularly those using the steroid for non-medical purposes. It is crucial for individuals considering or currently using testosterone propionate to be aware of the potential health risks, including the increased likelihood of developing diabetes.
Healthcare providers should also be vigilant in monitoring patients using testosterone propionate, especially those with pre-existing risk factors for diabetes, such as obesity or a family history of the condition. Regular screening for blood sugar levels and insulin resistance may be necessary to detect early signs of diabetes and initiate appropriate interventions.
Conclusion
The relationship between testosterone propionate and diabetes in American males is a complex and evolving area of research. While the evidence suggests a potential link between the use of this anabolic steroid and an increased risk of developing diabetes, further studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms involved and to establish definitive guidelines for its use.
American men should approach the use of testosterone propionate with caution, weighing the potential benefits against the possible health risks. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps to mitigate the risk of developing diabetes.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Hormonal Balance for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Male Fertility in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in American Sports: Ethical Issues and Health Risks for Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Role in Male Pattern Baldness Among American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Role in Weight Management for Obese American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Ethical Use in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Long-Term Health Risks of Testosterone Propionate Use in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Boosting Energy Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Therapy for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Use in American Male Bodybuilding [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Pain in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Aesthetic Use in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Psychological Effects and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Muscle, Energy, and Psychological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Cardiovascular Impact on American Men: Benefits, Risks, and Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Libido and Sexual Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Muscle Recovery in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Recovery and Performance in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits and Risks in Hormone Replacement Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Anemia in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Legal Issues for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate Use and Liver Health Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Bone Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Blood Pressure in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Endurance in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Immune System in American Men: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Muscle Wasting in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Legalities for American Weightlifters [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Stress Management Solution for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in Anti-Aging: Benefits, Risks, and Clinical Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Boosting Energy in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Managing Hormonal Imbalances in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Mood Swings in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Low Sperm Count in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Strength and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Uses, Benefits, and Risks in Male Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Uses, Benefits, and Risks for American Men's Health and Fitness [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Cardiovascular Effects and Risks in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Dosage, and Risks for American Men's Muscle Building [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Mental Health in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]