Introduction
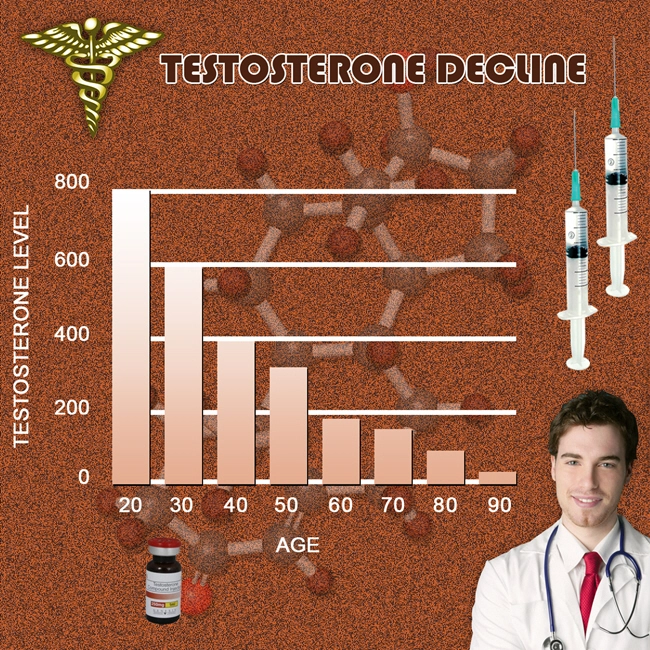
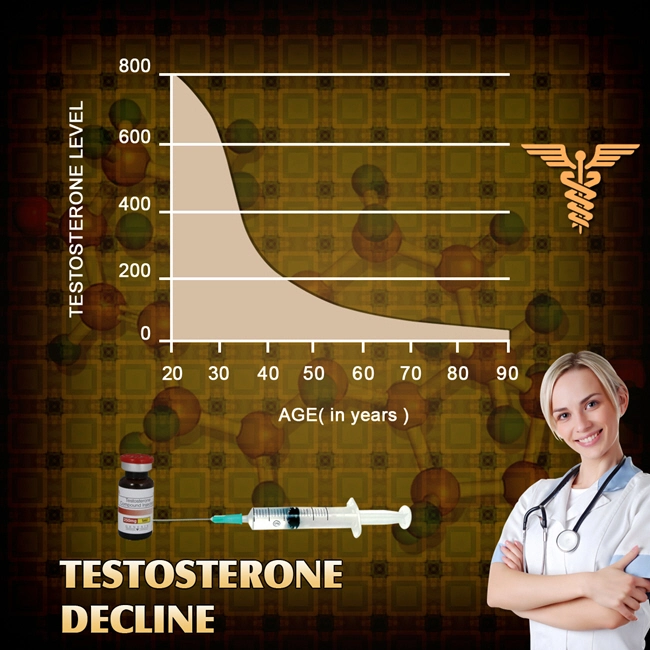
Testosterone deficiency, a prevalent condition among American men, has been increasingly recognized for its broad physiological implications. Recent studies have begun to explore its effects beyond traditional domains such as sexual health and muscle mass, venturing into the realm of urology. Specifically, the electrophysiological characterization of bladder afferent nerve activity in testosterone-deficient men offers a novel lens through which we can understand and potentially address urological symptoms associated with this condition.
The Role of Bladder Afferent Nerves
Bladder afferent nerves are crucial for the sensation of bladder filling and the initiation of micturition reflexes. These nerves transmit sensory information from the bladder to the central nervous system, playing a pivotal role in the coordination of bladder function. In men with testosterone deficiency, alterations in the activity of these nerves may contribute to urological symptoms such as urgency, frequency, and nocturia.
Electrophysiological Studies in Testosterone-Deficient Men
Recent research has utilized advanced electrophysiological techniques to record and analyze bladder afferent nerve activity in men with low testosterone levels. These studies have provided insights into how testosterone deficiency may alter nerve function, potentially leading to the urological symptoms observed in this population. The findings suggest that testosterone may play a role in modulating the sensitivity and responsiveness of bladder afferent nerves.
Key Findings and Implications
One of the key findings from these studies is the observation of increased afferent nerve firing rates in testosterone-deficient men, particularly in response to bladder distension. This heightened activity could explain the increased sensation of urgency and frequency reported by these individuals. Additionally, the studies have highlighted potential differences in nerve conduction velocities and thresholds for activation, further underscoring the impact of testosterone on bladder nerve function.
The implications of these findings are significant for the management of urological symptoms in American men with testosterone deficiency. By understanding the electrophysiological changes associated with this condition, healthcare providers can develop more targeted interventions, potentially improving quality of life for affected individuals.
Clinical Considerations and Future Directions
In clinical practice, the recognition of altered bladder afferent nerve activity in testosterone-deficient men underscores the importance of comprehensive urological assessments in this population. Screening for testosterone levels and considering hormone replacement therapy may be beneficial for managing associated urological symptoms.
Future research should focus on longitudinal studies to better understand the progression of these electrophysiological changes and their response to treatment. Additionally, exploring the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of testosterone on bladder afferent nerves could provide further insights into potential therapeutic targets.
Conclusion
The electrophysiological characterization of bladder afferent nerve activity in testosterone-deficient American men represents a significant advancement in our understanding of the urological implications of this condition. By shedding light on the intricate relationship between testosterone and bladder function, these studies pave the way for more effective management strategies, ultimately enhancing the well-being of affected individuals. As research in this field continues to evolve, it holds the promise of transforming the approach to urological care in men with testosterone deficiency.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Alpha1-Adrenoreceptor Density, Testosterone, and LUTS Severity in American Men: Current Insights [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Ultrastructural Implications of Testosterone Deficiency on Bladder Muscle: Electron Microscopy Insights [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Managing Urethral Epithelial Atrophy: Androgen Deficiency and Hormone Replacement Therapy Explained [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostate Stroma: Collagen and Elastin Dynamics Explored in Study [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Role of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase in Monitoring Androgen Activity During Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Men [Last Updated On: March 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 10th, 2025]
- Androgen-Dependent Regulation of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 in Prostatic Tissue: Implications for Male Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 10th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Impact of Hormone Replacement on Pelvic Floor Electromyographic Activity in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring Post-Void Residual Volume Changes in Men with Low Testosterone: A Longitudinal Study on Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring Urinary Proteomics in Androgen-Deficient Men: Unveiling New Biomarkers for Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Metabolomic Analysis of Prostatic Fluid in Testosterone-Deficient Men: Urological Insights [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Urinary Flow Cytometry Insights into Hypogonadism and Testosterone Therapy Effects [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Mitochondrial Function in Bladder Smooth Muscle: Urological Insights [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Androgen-Regulated Genes in Urothelium: HRT Impact and Urological Health Insights [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Prostatic Inflammation in Hypogonadal Men: Histopathology and TRT Benefits [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Vesicourethral Reflux in Hypogonadal Men: Bladder Neck Dysfunction and Hormonal Impact [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency's Impact on Lower Urinary Tract Autonomic Innervation: A Quantitative Analysis [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Aging Men's Prostate Health: Aromatase Activity, Testosterone Therapy, and BPH Risks [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate Health: Assessing Blood Flow with Color Doppler Ultrasonography [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Prostatic Neuroendocrine Cells in Androgen-Deficient Men: Analysis and HRT Response [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Kidney Stone Risk in American Men: Urine Sediment Patterns [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Neural Density in Detrusor Muscle of Hypogonadal Men: Clinical Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Impact on PSA Kinetics and Prostate Health Monitoring Protocols [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Hyperplasia in Hypogonadal Men: Morphometric Insights [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Urodynamic Insights into Detrusor Overactivity and Testosterone Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- UPP in Hypogonadal Men: Pre- and Post-ART Insights for Urologists [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate Health Monitored by Transrectal Shear Wave Elastography [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostatic Arterial Flow: Doppler Ultrasonography Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ultrasonographic BWT and Urodynamics in Men with Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- DSD in Androgen-Deficient Men: Prevalence, Urodynamics, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Function in American Men: Insights from AUM [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Influence on Bladder ECM: GAGs, PGs, and Men's Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Urinary Flow in Hypogonadal Men: Uroflowmetric and Hormonal Insights [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Non-Bacterial Prostatitis in Hypogonadal Men: Inflammatory Mediators [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency Impact on Urinary Flow: Urodynamic Analysis and Hormonal Insights [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Micturition Parameters in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Distribution in Lower Urinary Tract of Hypogonadal Men: Immunohistochemical Insights [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Urinary Exosomal miRNAs: Biomarkers for Monitoring LUTS Treatment in Hypogonadal American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Prostatic Calcifications in Hypogonadal Men: Prevalence, Composition, and LUTS Association [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Prostatic Urothelial Metaplasia in Hypogonadism: Prevalence and Testosterone Therapy Impact [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT and Prostate Health: Growth Factors and Hyperplasia in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Postvoid Dribbling in Testosterone-Deficient Men: Insights and Hormone Therapy Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostate Gap Junction Proteins and Health Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostate Cell Proliferation: A Histomorphometric Study [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bladder Neck Collagen and Urodynamic Function in Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- LOH Impact on Bladder Compliance in American Men: Urodynamic and Hormonal Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Nocturnal Polyuria in Testosterone-Deficient Men: Mechanisms and Hormone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy Improves Bladder Function in Hypogonadal Men: A Cystometric Study [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Androgen Therapy Modulates Apoptotic Index in Hypogonadal Men's Prostatic Epithelium [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency Impacts Bladder Function via Contractile Protein Expression in Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Neurogenic Bladder in Hypogonadal Men: Urodynamics, Hormones, and Clinical Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Effects on Prostatic Secretions: Biochemical Analysis and Health Implications [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Neurophysiological Impact of Testosterone on Bladder Sensory Afferents in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Detrusor Oxygenation in American Men with Androgen Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Urethral Sphincter EMG Changes in Hypogonadal Men Post-Testosterone Therapy: Urological Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy and PIN Incidence in Hypogonadal Men: Surveillance and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- PSMA Expression Analysis in Androgen-Deficient American Men Before and After ART [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostatic Smooth Muscle in American Men: Electron Microscopy Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Fluctuations in TRT and Maximum Urinary Flow Rate Variability in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Mapping Prostatic Stromal ARs in American Men with LUTS: Therapeutic and Diagnostic Insights [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Sensation: QST Insights Before and After HRT [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Estrogen's Role in LUTS: Prostatic Stromal Aromatase Activity in Aging Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Function: Impact and Improvement via HRT [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Urethral Function in Hypogonadal Men: UPP Topography Study [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- 3D Ultrasonography: Monitoring Prostate Health in Men on Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Wall Fibrosis: Impact and HRT Benefits in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Diurnal Testosterone Variations and LUTS in Hypogonadal Men: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Function: Myofibroblast Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Urology: Assessing Androgen Receptor Sensitivity in Prostatic Tissue [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Prostatic Elastography: Monitoring Prostate Health in Men on Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Benefits for Hypogonadal Men with Prostatitis-like Symptoms [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Overactive Bladder in Androgen-Deficient American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Power Doppler Ultrasonography Enhances TRT Monitoring in American Males' Urological Health [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Autophagy in Prostatic Cells of Hypogonadal American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Intraprostatic Hormone Fluctuations Before and During Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Mathematical Modeling Predicts Prostatic Growth in TRT for American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]