Introduction
Hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, has been increasingly recognized for its broader implications on health. Recent research has begun to uncover connections between hypogonadism and gastrointestinal health, an area of particular relevance to American males who may face higher risks due to lifestyle factors. This article delves into the medical connections between these two conditions, offering insights into how hypogonadism may influence gastrointestinal function and vice versa.
The Role of Testosterone in Gastrointestinal Health
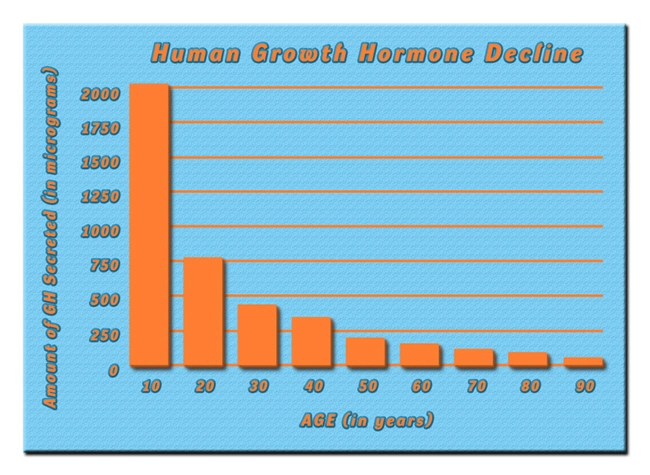
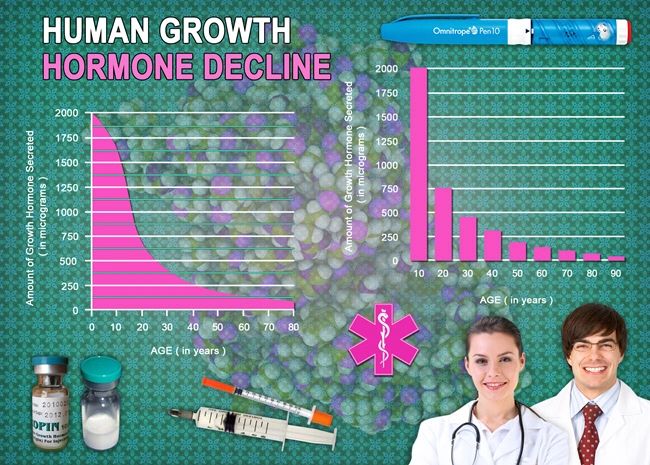
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the maintenance of muscle mass, bone density, and red blood cell production. Emerging studies suggest that testosterone also impacts gastrointestinal health. For instance, testosterone receptors have been identified in the gastrointestinal tract, indicating that the hormone may influence digestive processes and gut motility.
In American males, where hypogonadism prevalence is significant, the lack of adequate testosterone levels could potentially disrupt these gastrointestinal functions. Research has shown that low testosterone levels may lead to decreased gut motility, which can contribute to conditions such as constipation and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Impact of Gastrointestinal Disorders on Testosterone Levels
Conversely, gastrointestinal disorders can also affect testosterone levels. Chronic conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, are known to cause systemic inflammation, which can disrupt the body's hormonal balance. This inflammation may lead to hypogonadism by impairing the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which is responsible for testosterone production.
Moreover, malabsorption issues common in gastrointestinal disorders can lead to deficiencies in nutrients essential for testosterone synthesis, such as zinc and vitamin D. American males with chronic gastrointestinal conditions may therefore be at a higher risk of developing hypogonadism due to these nutritional deficits.
Clinical Implications and Management
Understanding the bidirectional relationship between hypogonadism and gastrointestinal health is crucial for effective management and treatment. For American males diagnosed with hypogonadism, it is essential to assess gastrointestinal function as part of a comprehensive health evaluation. Similarly, those with chronic gastrointestinal disorders should be screened for hypogonadism to address potential hormonal imbalances.
Treatment strategies may include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) for hypogonadism, which could also benefit gastrointestinal health by improving gut motility and reducing inflammation. Additionally, managing gastrointestinal conditions through dietary modifications, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory medications can help mitigate the risk of developing hypogonadism.
Lifestyle Considerations for American Males
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in both hypogonadism and gastrointestinal health. American males are often at risk due to sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, and high stress levels, all of which can contribute to both conditions. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in nutrients, and stress management techniques are essential for maintaining optimal testosterone levels and gastrointestinal function.
Incorporating foods high in zinc and vitamin D, such as lean meats, fish, and fortified cereals, can support testosterone production and overall health. Probiotics and fiber-rich foods can also promote a healthy gut microbiome, which is vital for digestive health.
Conclusion
The connection between hypogonadism and gastrointestinal health is a critical area of study, particularly for American males. By recognizing the interplay between these conditions, healthcare providers can develop more holistic treatment plans that address both hormonal and digestive health. As research continues to evolve, it is hoped that these insights will lead to improved outcomes for American males facing these intertwined health challenges.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 24th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Best Practices in Monitoring Hypogonadism: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Sleep Disorders: A Bidirectional Impact on Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Muscle Health Dilemma: The Role of Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Navigating Hypogonadism in Men with Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Impaired Wound Healing in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Connection Between Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy in Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Liver Health: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Medical Education Essentials [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Chronic Pain: Integrated Treatment Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Thyroid Function: Interplay and Impact on Male Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Disorders: Insights and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Ethical Challenges in Diagnosing and Treating Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Prostate Health: Understanding and Managing Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Screening and Management Guidelines for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men: Physical, Mental, and Social Effects [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cancer Risk: Understanding Links and Managing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Medical Imaging's Crucial Role in Diagnosing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Health in American Males: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Health and Therapeutic Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Health: Treatments and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism and Kidney Disease in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Innovations in Hypogonadism Treatment: From TRT to Personalized Medicine [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Preventing Hypogonadism in American Males: Strategies and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health and Testosterone Replacement Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Blood Pressure: Understanding Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Medical Rehabilitation for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Headaches: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Monitoring Hypogonadism in Long-Term Care: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Joint Health and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Multidisciplinary Medical Teams [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Neurological Disorders in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact on Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Psychological Counseling Needs for American Males with Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Anemia in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Dental Health: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact: Understanding and Managing Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cholesterol: A Critical Link Impacting Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Promising Approach to Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Trends, Treatments, and Future Research Directions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Understanding Links and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hearing Loss: Exploring the Link and Implications for Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Transgender Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Technology's Role in Diagnosing Hypogonadism: Advances and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Balance: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Allergies: Exploring the Medical Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Eye Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Vision: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism-Related Fatigue: Therapies and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and GERD: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in Primary Care: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Monitoring Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Medical Social Workers: Vital Support for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]