Introduction
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low testosterone levels due to dysfunction in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, can significantly impact a man's quality of life, particularly in terms of sexual function. Among the therapeutic options available, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) monotherapy and testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) are commonly considered. This article delves into the comparative effects of these treatments on erectile function in American males suffering from this condition.
Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism
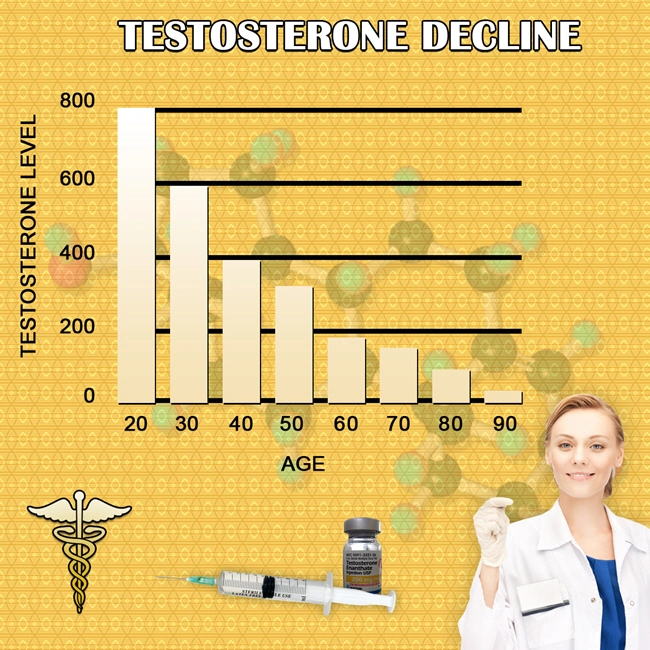
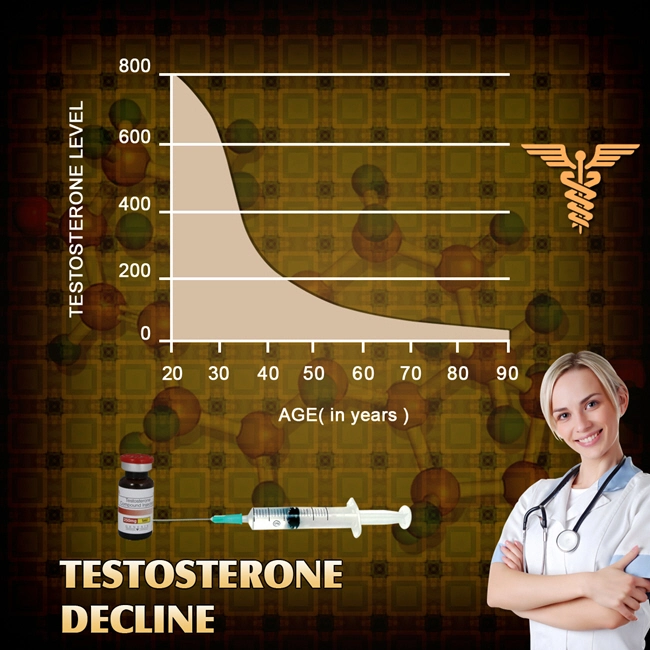
Secondary hypogonadism, also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, results from inadequate stimulation of the testes due to pituitary or hypothalamic dysfunction. This leads to decreased testosterone production, which can manifest as reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and other symptoms that can severely affect a man's sexual health and overall well-being.
hCG Monotherapy: Mechanism and Effects
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone that mimics luteinizing hormone (LH), stimulating the Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone. hCG monotherapy aims to restore the body's natural testosterone production without suppressing the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Studies have shown that hCG can improve erectile function in men with secondary hypogonadism by increasing testosterone levels and potentially preserving fertility.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Mechanism and Effects
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) involves the administration of exogenous testosterone to increase serum testosterone levels directly. While effective in alleviating symptoms of hypogonadism, TRT can suppress the body's natural production of testosterone and may impact fertility. TRT has been shown to improve erectile function in men with hypogonadism, but its long-term effects and potential side effects require careful monitoring.
Comparative Analysis of hCG and TRT on Erectile Function
Both hCG monotherapy and TRT have been demonstrated to enhance erectile function in men with secondary hypogonadism. However, the mechanisms by which they achieve this differ significantly. hCG works by stimulating endogenous testosterone production, which may offer the added benefit of preserving fertility. In contrast, TRT directly increases testosterone levels but may lead to testicular atrophy and reduced sperm production.
Clinical studies comparing the two treatments have yielded mixed results. Some research suggests that hCG may be more effective in improving erectile function in younger men or those with milder forms of hypogonadism, while TRT may be more suitable for older men or those with more severe symptoms. Additionally, the choice between hCG and TRT may depend on the patient's fertility goals and overall health status.
Considerations for American Males
For American males, the decision between hCG monotherapy and TRT should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, taking into account individual health goals, fertility concerns, and potential side effects. Regular monitoring of testosterone levels, sperm count, and overall health is crucial to ensure the chosen treatment remains effective and safe.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both hCG monotherapy and testosterone replacement therapy offer viable options for improving erectile function in men with secondary hypogonadism. While hCG may preserve fertility and stimulate natural testosterone production, TRT provides a direct increase in testosterone levels but may have long-term implications for fertility and testicular function. American males facing this condition should work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment based on their individual needs and health objectives.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Exploring Vasopressin Receptor Antagonists: A Breakthrough in Treating Sexual Dysfunction in Eugonadal Men [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Somatostatin Analogues' Impact on Sexual Function in American Men with Neuroendocrine Disorders [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Kisspeptin in Men with Hypothalamic Hypogonadism: Impacts on Sexual Function and Desire [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Optimizing Hormone Replacement Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: The Cortisol-Testosterone Ratio Connection [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Neurosteroid Modulation: A Promising Treatment for Men's Libido Disorders and Beyond [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Managing Hormonal Imbalances in Men with Aromatase Inhibitors: Improving Sexual Health Safely [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Enhancing Male Sexual Health: The Role of DHEA Supplementation in Combating Age-Related Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring Melatonin's Impact on Circadian Rhythms and Sexual Health: A Case for Integrated Hormone Therapy in American Males [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- SARMs' Impact on Sexual Function in Aging American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Polymorphisms in Androgen Receptors Impact Hormone Therapy for Male Sexual Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Leptin Resistance and Sexual Dysfunction in Men: Insights from Hormone Optimization Therapy [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Enhancing Erectile Function via Endothelial and NO Pathways [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Zinc Supplementation Enhances Testosterone Therapy for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- TRT Pharmacokinetics and Sexual Function in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Age-Related Decline in Kiss1 Expression and Its Impact on Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Ghrelin's Dual Role in Appetite and Sexual Health: Interventions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Bioavailable vs. Total Testosterone: Predicting Sexual Function in HRT for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Vitamin D, Testosterone Levels, and Erectile Function: Clinical Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Clinical Trial Reveals GnRH Modulation Therapy Effective for HSDD in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Timing of HRT Crucial for Sexual Function in American Males with Delayed Puberty [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Iodine Deficiency, Thyroid Health, and Male Sexual Function: Multimodal HRT Benefits [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Calcium-to-Magnesium Ratio's Impact on HRT Success in American Men with Sexual Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Pituitary Microadenomas: Impact on Male Sexual Health and Hormone Therapy Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Mumps Orchitis and Sexual Dysfunction: Efficacy of Hormone Replacement in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Magnesium Levels Predict Testosterone Therapy Success for ED in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Anabolic Steroid-Induced Hypogonadism: Recovery and Sexual Health Restoration in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Chromium Supplementation Enhances Testosterone Therapy: Benefits for Insulin Sensitivity and Sexual Function [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapies for Sexual Function in American Males with Testicular Atrophy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Phlebotomy and HRT Improve Sexual Function in Males with Iron Overload and Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Therapy Responses in Testicular Failure vs. Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Selenium's Role in Male Sexual Health: Hormonal Balance and Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Comparing Hormone Replacement Strategies for Chemotherapy-Induced Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism's Impact on Testosterone and Sexual Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Radiation-Induced Testicular Damage: Effects on Sexual Function and Hormone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Copper-to-Zinc Ratio: Predicting Hormone Therapy Success in Male Sexual Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes and Sexual Health: Metabolic Control and Hormone Optimization [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Opioid-Induced Endocrinopathy: Comparing Hormone Replacement Therapies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Boron Supplementation Enhances Sexual Function in Aging American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Cryptorchidism: Impacts on Sexual Function and Modern Hormone Therapy in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Traumatic Testicular Injury: HRT Benefits and Risks for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Varicocelectomy with Hormone Therapy Enhances Sexual Function in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HRT Improves Sexual Function in Aging Males with PADAM: Long-Term Outcomes [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Abstinence and Hormone Therapy Enhance Sexual Health in American Males with Alcohol-Induced Testicular Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testicular Torsion's Impact on Sexual Function and Hormone Optimization Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males with CKD: Benefits and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Phlebotomy and Testosterone Therapy Enhance Sexual Function in Hemochromatosis-Induced Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Weight Loss vs. HRT: Managing Obesity-Related Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Optimizing Hormone Therapy for Sexual Dysfunction in Klinefelter Syndrome: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Glucocorticoid vs. Testosterone Therapy: Managing Sexual Dysfunction in Adrenal Insufficiency [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Sexual Dysfunction in American Males: Combined Therapy Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Marijuana Use and Male Sexual Health: Hormonal Impacts and HRT Solutions [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- NAFLD in American Males: Hormonal Dysregulation, Sexual Health, and Multimodal Treatment [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Sexual Health in American Males: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Cushing's Syndrome: Cortisol, Testosterone Therapy, and Sexual Health Recovery in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- CPAP and Hormone Therapy Enhance Sexual Health in Men with OSA [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- IBD's Impact on Testosterone and Sexual Health in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Parkinson's Disease Impact on Sexual Health in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Dopamine Agonists vs. Testosterone for Hyperprolactinemia-Induced Sexual Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Exploring MS Impact on Male Sexual Health: Neurohormonal Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Alzheimer's Impact on Sexual Health in American Males: Exploring HRT and Holistic Care [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Innovative SCI Treatments: HRT and Neuromodulation Restore Sexual Function in American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Post-Stroke Sexual Dysfunction in American Men: Neuroendocrine Assessment and Hormone Therapy Outcomes [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- HRT as a Promising Solution for SSRI-Induced Sexual Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Mitigating Sexual Dysfunction in Prostate Cancer Treatment with Selective Hormone Replacement [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Antipsychotic-Induced Hyperprolactinemia: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Beta-Blockers' Impact on Sexual Function in American Males: Comparative Study and Hormone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Recovery from 5?-Reductase Inhibitor Sexual Dysfunction: Hormone Modulation Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Statins and Male Sexual Health: Hormonal Impacts and Testosterone Therapy Solutions [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Clomiphene Citrate vs. TRT: Impacts on Sexual Function and Fertility in Young Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Post-Prostatectomy Sexual Health: HRT Timing, Types, and Holistic Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Radiotherapy-Induced Endocrine Dysfunction: Managing Sexual Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Partial Hormone Replacement: Enhancing Sexual Function in Prostate Cancer Patients on ADT [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Challenges and Aromatase Inhibitors' Role in Sexual Health [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]