Video Link: https://vimeo.com/285651895
Video Download: Click Here To Download Video
Video Stream: Click Here To Stream Video
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/285651818
Video Download: Click Here To Download Video
Video Stream: Click Here To Stream Video
The definition of fasting is uncomplicated: voluntarily not eating solid food or drinking calorie-containing beverages for a specified period. The practice of fasting has been done for thousands of years for a broad range of reasons.
There are several well-known health benefits of fasting. Here is a list of many of them:
- Fasting improves cognitive functioning. Fasting can make your brain function at a higher, more efficient level. This mental boost is due to an increase of neurons that deliver protection to the mind. This higher functioning makes sense when we consider evolution. Our ancient ancestors survived because their brains functioned well when they needed to find food.
- Fasting strengthens the immune system. Fasting causes cellular regeneration by signaling stem cells to manufacture new white blood cells and replace blood cells that have become senescent (old and tired). The result of this process is a reboot of your immune system.
- Replace white fat with brown fat. Many people are unaware that there are two types of fat in the body: white fat and brown fat. Brown fat burns energy,
 while white fat stores energy that eventually may turn into the kind of fat that is both unsightly and unhealthy. White fat is also known as visceral fat and is found in the mid-section. Studies have indicated that fasting plays a role in changing white fat into brown fat, which is a far more efficient energy source.
while white fat stores energy that eventually may turn into the kind of fat that is both unsightly and unhealthy. White fat is also known as visceral fat and is found in the mid-section. Studies have indicated that fasting plays a role in changing white fat into brown fat, which is a far more efficient energy source. - Fasting causes better digestion. Why? Because your internal organs need an occasional break from their continuous task of breaking down and absorbing food. Fasting gives those overworked organs a bit of rest.
- Fasting promotes weight loss. This should not require much explanation. Fewer calories taken in means the pounds drop off. After you eat, your insulin levels rise, and you do not need to use fat for energy since your body relies on food to keep you going. But several hours after you stop eating, there is no food for the body to use. At that point, the body is forced to burn fat, and the pounds begin to melt.
- A right kind of weight loss. Studies have demonstrated that intermittent fasting causes less muscle loss than regular dieting. A 2011 survey found that 90% of the weight loss obtained through intermittent fasting was fat, as opposed to 75% from regular dieting.
- Fasting increases insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance is a severe health problem. When this condition is present your cells are unable to soak up excess glucose from your blood. If this continues, the result is diabetes -- something no one wants or needs. Fasting solves this condition by freeing up more insulin by forcing the body to use fat cells for energy. Going longer between meals lets the body pump out less insulin. Also, after fasting, the body becomes more sensitive to insulin.
- Fasting may also boost neurological disease protection from devastating conditions like Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Dementia. Dr. Mark Mattson, chief of the neurosciences lab at the National Institute of Aging (NIA) said that “Just as exercise makes muscles stronger, fasting makes the brain stronger.”
- Fasting may improve cholesterol and triglyceride levels and lower blood pressure.
- Fasting can sweep cholesterol from the veins and arteries. A study conducted at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Utah found that after a mere one-day fast every week for six weeks, the participant's baseline cholesterol levels fell by 12%. The reason? The body switches its energy source from blood sugar to fat. Burning fat cells lowers cholesterol, for the same reason that fasting fights diabetes.
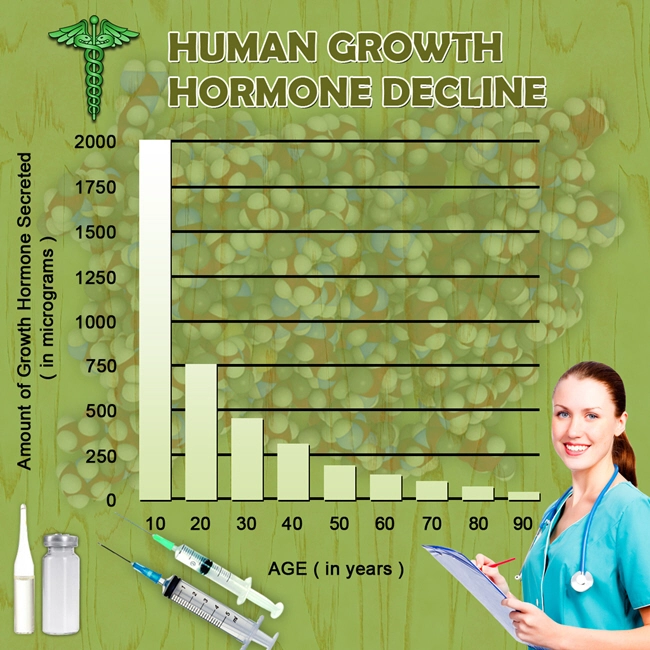
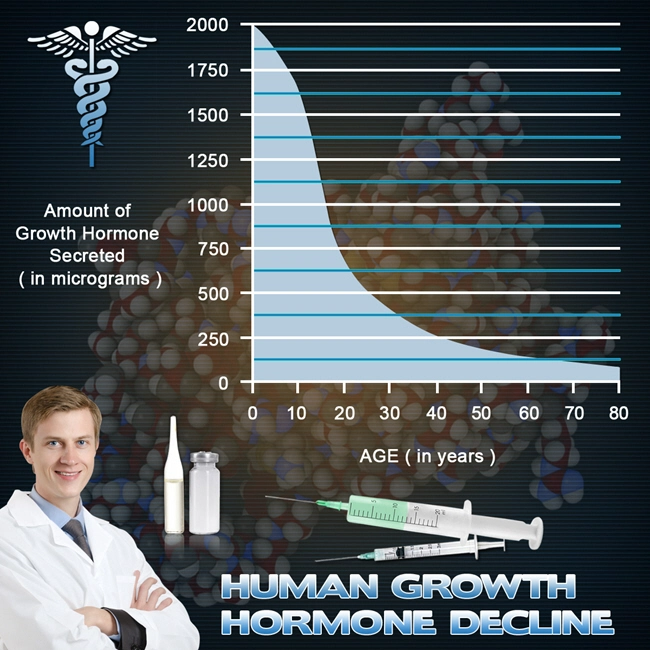
- Fasting may also boost Human Growth Hormone (HGH) levels.
Why Fasting Works: Science Combines with Evolution
During a fast, your body enters autophagy, which is a condition that eliminates cellular waste by breaking down proteins and removing toxins that accumulate in your cells.
 This toxin removal is where the anti-aging benefits begin. The body, in its innate wisdom, will first throw out the cells that have been damaged by illness or aging. Researchers state that fasting can turn the ignition key to cause the body to break down old white blood cells (the body’s defenders from disease) and build new, rejuvenated white blood cells.
This toxin removal is where the anti-aging benefits begin. The body, in its innate wisdom, will first throw out the cells that have been damaged by illness or aging. Researchers state that fasting can turn the ignition key to cause the body to break down old white blood cells (the body’s defenders from disease) and build new, rejuvenated white blood cells.
The body uses glycogen for energy. This glycogen has been stored in the muscles and the liver and remains there until it is needed. When the body is unable to satisfy its need for glucose from food, it reaches into the supply of liver glycogen. This glycogen is used to control insulin and gather free fatty acids for fuel.
This explains why fasting leads to fat loss. Long-chain fatty acids have trouble when trying to cross the blood-brain barrier. This barrier causes the body to break these fatty acids down by a process called beta-oxidation, which creates ketone bodies to be used as energy for both the brain and the muscles.
This use of ketones is crucial since studies have demonstrated that ketones are 70% more efficient at delivering energy than glucose.
As a result of this efficiency, Growth Hormone levels explode by as much as five times!
Another study concluded that fasting could result in a 1,000% spike in Growth Hormone.
Research conducted by the Intermountain Medica concluded that Intermittent Fasting (IF) could dramatically boost Growth Hormone levels. In a recent study, men who fasted for 24 hours saw a 2,000% rise in Growth Hormone, and women in the study benefited from a 1,300% increase.
More good news: Researchers have concluded that the benefits of fasting can be achieved by fasting as few as eight days a year.
Research from the USC Davis School of Gerontology determined that fasting for two to four days at a time can reinvigorate the entire immune system.
Always remember that the body needs energy from some source, even if it’s not food. When food is removed from the equation, the energy source sequence is fat, muscles, and organs. HGH protects muscles. The body possesses the knowledge to know when the food supply stops and adjusts accordingly by ramping up the production of HGH.
This adjustment means that fat will be used first as energy before muscle. And don’t worry about your organs; if you are in the final stages of starvation, you will be long dead before your organs are used for energy.
To keep things somewhat simple, remember this formula: When the amount of fat the body uses for energy rises, the need for glucose as an energy source decreases. As fat use for energy increases, sugar used for energy drops.
This is crucial since this process stabilizes blood glucose levels. This method also explains why muscle mass does not tumble. Since the body requires less glucose, there is no need for the body to cannibalize muscle tissue to produce new glucose.
When done correctly and precisely, eating slows the release of HGH, and fasting speeds up the release of HGH.
Also, the body’s ability to use fat for energy while fasting is a product of hundreds of thousands, if not millions of years of evolution. The easy availability of  food is a recent development. Throughout recorded history, there have been periods where food supplies were scarce. This led to an “adapt or perish” survival mode and accounts for the body’s massive release of Growth Hormone during fasting to protect muscle tissue.
food is a recent development. Throughout recorded history, there have been periods where food supplies were scarce. This led to an “adapt or perish” survival mode and accounts for the body’s massive release of Growth Hormone during fasting to protect muscle tissue.
However, the timeframe for Growth Hormone release is finite. Studies have demonstrated that after approximately 48 hours without food Growth Hormone levels will begin to taper off. Therefore, intermittent fasting is the technique you need to employ. Here’s why.
The body’s fight-or-flight hormones are called Epinephrine and Norepinephrine and are also called adrenaline and noradrenaline, or “catecholamines.” When fasting, the body is under stress, and this triggers the adrenal glands to release these hormones.
When these “stress hormones” enter the blood they provoke the release of glucose which has been stored as an energy source. This process increases fat-burning.
As mentioned above, the time for beneficial Growth Hormone is limited. If the body is forced into a flight-or-flight mode for an extended period, adrenal fatigue follows, resulting in catabolic stress.
Catabolic stress is a debilitating condition that results in protein loss, a break down of muscle protein, unhealthy rapid weight-loss, and possible organ problems.
The key is balance. Not too much stress, or not too little. And that is precisely what intermittent fasting delivers.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Before we continue, a definition of intermittent fasting is in order. Intermittent Fasting (IF) is a blanket term for a variety of eating plans that cycle between fasting and not fasting for a limited time. It is not going without food for extended periods (weeks or months).
There are several types of IF. Here is a brief description of the most common approaches:
Intermittent Fasting Options
There are several methods of intermittent fasting. Here are a few of the most popular ways:
- The “16/8 method.” This approach is simple: In a 24-hour period, only eat in an eight-hour window, and refrain from eating in the other 16 hours in the day. The hours you choose are irrelevant; it is the numbers that count. Skip breakfast or lunch, depending on your preference.
- The “5/2 method.” This approach means that you eat as usual five days a week, and on the other two days restrict your calories to 500.
- The “One-Day” approach means stop eating after the evening meal on one day, then do not eat the following day and only resume eating at breakfast on
 the third day. For example, Tuesday night’s meal will be the last solid food until Thursday morning’s breakfast. This approach allows some flexibility; many followers of this path drink a blend of coffee, butter, and MCT oil to speed up ketosis.
the third day. For example, Tuesday night’s meal will be the last solid food until Thursday morning’s breakfast. This approach allows some flexibility; many followers of this path drink a blend of coffee, butter, and MCT oil to speed up ketosis. - Another IF method is the “Every Other Day Diet,” where you rotate every other day between fasting and regular eating.
- Still another approach to intermittent fasting is the “Fast Mimicking Diet” (FMD). This method involves fasting for a 5-day period on a monthly cycle. However, the five fasting days are not entirely without food. Instead, on those days, the dieter follows a low-calorie diet consisting of 25-50% of their usual calorie intake, approximately 10% protein, and the rest split between fats and carbs.
There are still other, far more radical methods. These involve fasting for as much as a week at a time, or even longer. This is, to put it mildly, far too extreme for the average person.
Also, a long-term fast can boomerang by slowing your metabolism, thus sabotaging the weight-loss goals that made you consider intermittent fasting in the first place.
However, as mentioned earlier, the benefits of IF do not require such extremes.
Many people have reported dropping both pounds and inches while following these different methods.
Some feel that folks that are doing IF will ruin their efforts by overeating on their usual eating days. Surprisingly, this seldom happens. According to Dr. Krista Varady, author of Every Other Day Diet, “Something keeps people from really binging on that feed day. We’re seeing that people in the every-other-day-group are losing more weight -- about 5 to 7 pounds more -- because they’re just able to stick with it longer. They like that they’re always able to look forward to the next day when they can eat whatever they want.”
Another bonus of intermittent fasting: for people who have trouble following a strict diet, IF is what they have been looking for. They don’t have to stress over what they can’t eat and what they are allowed to eat. They only need to focus on staying on their IF schedule.
Also, intermittent fasting helps restore a more normal hormonal balance, which is excellent for folks who feel like they’re always starving.
IF excels at helping folks lose that stubborn fat and those last few diet-resistant pounds.
Still another benefit of intermittent fasting is that some of the time during the fast is spent sleeping, which also boosts Growth Hormone.
Intermittent fasting is also convenient. There are no dramatic revisions to your existing eating habits. You just choose a day or two during the week to restrict your calories.
Exercise and Intermittent Fasting
A question often arises with people new to IF: what about exercise? Is it safe to exercise while fasting?
 The answer is a resounding yes! A recent 12-week study compared three groups: one group that only exercised, one group that just intermittently fasted, and the third team that combined both approaches.
The answer is a resounding yes! A recent 12-week study compared three groups: one group that only exercised, one group that just intermittently fasted, and the third team that combined both approaches.
There was a more substantial decline in both pounds and inches in the combined group compared to the fasting and exercise groups.
Also, in the combination group, the high-density lipoprotein (HDL, “the good cholesterol”) went up, and the low-density lipoprotein (LDL, “the bad cholesterol”) dropped. The fasting-only group experienced a decline in LDL, while the exercise-only group did not see a drop in LDL.
The takeaway? The combination of intermittent fasting and exercise will help you to burn more fat and preserve more lean muscle tissue. A double win!
Who Should Not Consider Intermittent Fasting
In spite of its many potential benefits, intermittent fasting is not for everyone. If you love to gorge on refined carbohydrates, you are probably experiencing a rise in your blood sugar levels a long with an insulin spike. This means that you could be challenged on fasting days by hunger and irritability.
If you have had a prior eating disorder such as bulimia or anorexia IF is probably not a good path for you to follow, since it may raise the risk of returning to your sickness.
Also, pregnant women need not apply since pregnancy is not the time to concentrate on burning fat.
Caution: If you suffer from diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or other metabolic conditions, or you are currently taking any prescribed medications, do not fast until you have discussed this with your physician.
Our clinic is dedicated to providing you with the most comprehensive Growth Hormone replacement program available. 
This includes the latest cutting-edge techniques, the most excellent Growth Hormone in the world, nutritional and physical advice, and anything else that will ensure you receive the maximum benefit from Growth Hormone replacement.
And that includes our guidance on the fascinating link between Growth Hormone and intermittent fasting.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Obese Patients Have a Higher COVID-19 Mortality Risk Than the General Public [Last Updated On: January 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 21st, 2020]
- The Health and Hormone Balancing Qualities of Broccoli [Last Updated On: August 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 27th, 2020]
- What to eat to boost testosterone [Last Updated On: September 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 14th, 2020]
- Breaking a Weight Loss Plateau: How to Reduce Body Fat When Nothing Seems to be Working [Last Updated On: January 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 16th, 2021]
- The Top 25 Most Nourishing and Sustaining Foods to Add to Your Diet Today for Increased Longevity [Last Updated On: January 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 16th, 2021]
- Fight Inflammation and Osteoporosis with Beets! [Last Updated On: January 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2021]
- Break a Weight Loss Plateau with Apple Cider Vinegar [Last Updated On: January 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2021]
- Health Reasons for a Vegan Diet [Last Updated On: October 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2021]
- Leafy Greens are Medicine for Your Gut [Last Updated On: September 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2021]
- All Praise to the Spud -- the Delicious, Health-Giving Potato, That Is [Last Updated On: August 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 1st, 2021]
- 16 Cancer-Causing Foods to Avoid [Last Updated On: May 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 12th, 2021]
- Longevity and Anti-Aging -- The Use of Flax Seed Oil [Last Updated On: May 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 17th, 2021]
- Essential Amino Acids Critical to Health and Hormone Balance [Last Updated On: June 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 6th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Calcium [Last Updated On: January 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 16th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Coffee [Last Updated On: January 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2021]
- The Importance of Protein in Weight Loss and Testosterone Production [Last Updated On: January 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2021]
- Testosterone, Growth Hormone, and Sugar. [Last Updated On: January 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2021]
- Testosterone, Growth Hormone, and Processed Meat [Last Updated On: January 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Intermittent Fasting [Last Updated On: January 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and the Importance of Nutrition [Last Updated On: January 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone Stops Inflammation! [Last Updated On: January 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Sugar Addiction [Last Updated On: January 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Red Meat [Last Updated On: January 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2021]
- Boost Growth Hormone with Sleep [Last Updated On: May 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2021]
- A Natural Acid Found in Apples Prevents Muscle Loss AKA Sarcopenia [Last Updated On: January 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Organic Foods. [Last Updated On: January 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Acidosis [Last Updated On: January 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2021]
- Growth Hormone Food Choices [Last Updated On: January 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Cholesterol: the Surprising Link [Last Updated On: January 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 22nd, 2021]
- Growth Hormone and Weight Loss [Last Updated On: January 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 22nd, 2021]
- Growth Hormone Reduces Inflammation [Last Updated On: January 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2021]
- What You Eat Impacts Both Your Sleep AND Your Growth Hormone Production [Last Updated On: January 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2021]
- Growth Hormone Lowers Blood Sugar [Last Updated On: January 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2021]
- Testosterone and Magnesium [Last Updated On: May 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 28th, 2022]
- The Beneficial Functions of Brown Fat vs. White Fat [Last Updated On: May 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 3rd, 2022]
- MOTS-c Peptide for Weight Loss and Muscle Building [Last Updated On: June 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 7th, 2022]
- Looking to lose weight? Add this ingredient to meals [Last Updated On: September 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 7th, 2022]
- The many health benefits of black tea [Last Updated On: September 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 13th, 2022]
- Raw Food Benefits [Last Updated On: September 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 18th, 2023]
- Brain Foods that Work Together with HGH to Improve Mental Sharpness [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2024]