Introduction
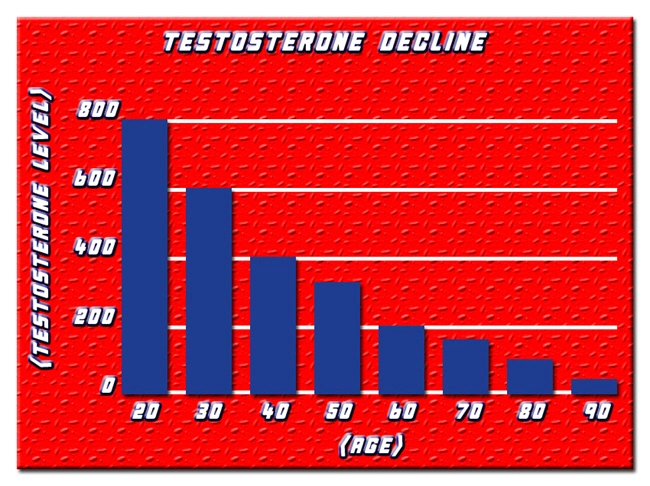
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has become increasingly common among American males seeking to address symptoms associated with low testosterone levels, such as reduced libido, fatigue, and muscle loss. Among the various formulations available, Depo Testosterone, manufactured by Pfizer, is a widely used injectable form of testosterone cypionate. While TRT can offer significant benefits, concerns regarding potential side effects, particularly on liver function, have prompted further investigation. This article delves into a retrospective analysis examining the correlation between Depo Testosterone Pfizer use and liver function in American males, aiming to provide a clearer understanding of its safety profile.
Background on Depo Testosterone Pfizer
Depo Testosterone Pfizer is an injectable testosterone cypionate used to treat conditions resulting from low testosterone levels in men. Administered intramuscularly, it is designed to provide a sustained release of testosterone into the bloodstream, thereby maintaining stable hormone levels. Despite its effectiveness, the potential impact on liver function remains a critical area of concern, as the liver plays a pivotal role in metabolizing hormones and drugs.
Methodology of the Retrospective Analysis
The study analyzed medical records of American males who had been prescribed Depo Testosterone Pfizer over a five-year period. Liver function was assessed through regular monitoring of liver enzymes, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). These enzymes serve as biomarkers for liver health, with elevated levels indicating potential liver damage or dysfunction.
Findings on Liver Enzyme Levels
The analysis revealed that the majority of participants maintained stable liver enzyme levels throughout their treatment with Depo Testosterone Pfizer. However, a small subset of individuals exhibited transient elevations in ALT and AST, which returned to normal ranges upon further monitoring. Importantly, no cases of severe liver toxicity or liver failure were reported among the study participants. These findings suggest that while Depo Testosterone Pfizer may cause temporary fluctuations in liver enzyme levels, the risk of significant liver damage appears to be low.
Comparison with Other Testosterone Formulations
To contextualize the results, the study also compared the liver function outcomes of Depo Testosterone Pfizer users with those using other testosterone formulations, such as oral testosterone undecanoate and transdermal gels. The data indicated that injectable testosterone cypionate, like Depo Testosterone Pfizer, generally had a lower impact on liver enzymes compared to oral formulations, which are known to undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver.
Clinical Implications and Recommendations
Based on the findings, healthcare providers can reassure patients that Depo Testosterone Pfizer is generally safe with respect to liver function. However, regular monitoring of liver enzymes remains essential, particularly for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking other medications that may affect liver health. Patients should be counseled on the importance of adhering to scheduled follow-up appointments and reporting any symptoms suggestive of liver dysfunction, such as jaundice or abdominal pain.
Limitations and Future Research Directions
While this retrospective analysis provides valuable insights, it is not without limitations. The study relied on existing medical records, which may not capture all relevant variables influencing liver function. Future research should include prospective studies with larger sample sizes and more comprehensive data collection to further validate these findings. Additionally, exploring the long-term effects of Depo Testosterone Pfizer on liver health could offer additional clarity on its safety profile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the retrospective analysis of Depo Testosterone Pfizer use among American males suggests that the therapy is generally well-tolerated with respect to liver function. While transient elevations in liver enzymes may occur, the risk of severe liver damage appears to be minimal. These findings underscore the importance of ongoing monitoring and personalized patient care in managing testosterone replacement therapy. As research continues to evolve, healthcare providers and patients can make more informed decisions regarding the use of Depo Testosterone Pfizer and its impact on liver health.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men with Pfizer's Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- American Men's Experiences with Pfizer's Depo Testosterone Therapy: Benefits and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Therapy: Tailoring Treatment for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Men's Health with Pfizer's Injectable Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Efficacy, Safety, and Patient Satisfaction in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Challenges and Solutions for American Men's Access to TRT [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Psychological Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Therapy: Innovations and Future in American Male Healthcare [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Chronic Conditions in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Delayed Puberty in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo-Testosterone's Impact on Weight Management in American Males: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Energy and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo-Testosterone: Benefits and Risks for Older American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Considerations for Transgender American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Hair Loss Risks in American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Sleep and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits, Risks, and Prostate Health Considerations [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Male Fertility and Preservation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Joint Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Mood and Well-being in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Adolescent Hypogonadism with Informed Care and Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits, Risks, and Legal Issues for American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Usage, Dosage Adjustment, and Monitoring for Optimal Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Blood Sugar Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Depo Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Skin Health and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits for Hypogonadism and Liver Health Considerations [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Performance and Health in American Male Weightlifters [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Cardiovascular Risks and Benefits in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone by Pfizer: Enhancing Male Libido and Sexual Function through TRT [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Body Composition and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men with Pfizer's HRT [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Veterans' Health and Well-being with Pfizer's Treatment [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Guide for American Males Treating Infertility [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Immune System and TRT Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life for American Male Cancer Survivors [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Potential Solution for Stress Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Anemia Treatment in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life Quality for American Males with HIV/AIDS [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Osteoporosis in American Males - Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Treating Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Safety and Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Eye Health Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Key Therapy for Managing Thyroid Disorders in Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Diabetes in American Males - Benefits and Research Insights [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: Insights and Recommendations [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Novel Approach to Managing Anxiety in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone by Pfizer: Impacts on Ear Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Exploring Its Potential in Managing Allergies Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Skin Health and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Migraines in American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Arthritis in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Insomnia in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Pfizer: Managing Autoimmune Diseases in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Cardiovascular Benefits and Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Potential in Managing Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Respiratory Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Dermatological Conditions in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Genetic Disorders in American Males - Efficacy, Dosage, Side Effects [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on American Males' Reproductive Health and Fertility [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Renal Health in American Males with TRT [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Inflammatory Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Metabolic Health in American Males with Pfizer's Therapy [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Musculoskeletal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Role in Managing Urological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Hematological Health in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Pfizer: Impacts on Psychiatric Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Cancer Risks in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Exploring Its Role in Managing Infectious Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effective Low Testosterone Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]