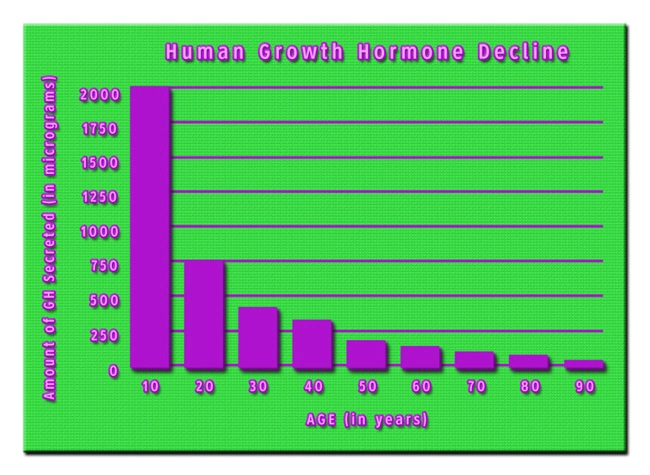
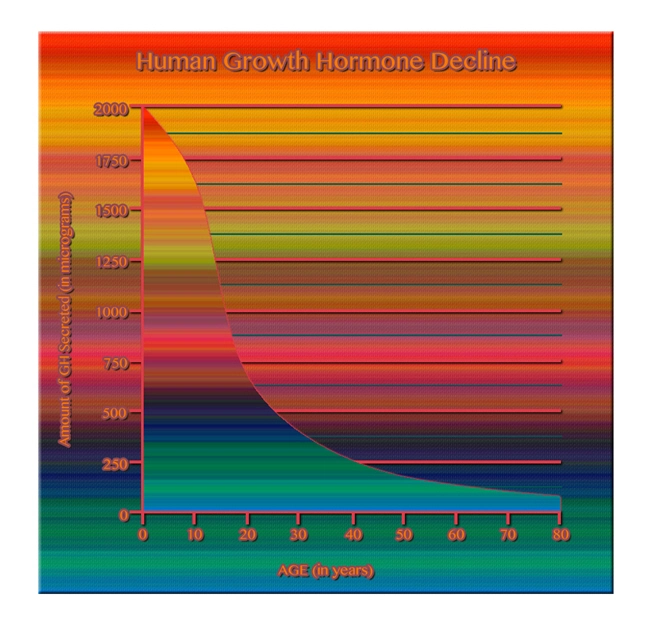
Introduction
The intricate relationship between sexual health and overall well-being is an area of growing interest within the medical community. For American males, the convergence of low libido and weight gain presents a compelling hypothesis that warrants further exploration. This article delves into the potential connections between these two conditions, offering insights into their possible interdependence and the implications for men's health.
Understanding Low Libido
Low libido, or a diminished sexual desire, is a common concern among American males. It can stem from various factors, including hormonal imbalances, psychological stress, and lifestyle choices. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in regulating libido. When levels of this hormone decrease, men may experience a decline in sexual interest and performance.
The Impact of Weight Gain
Weight gain, particularly when it leads to obesity, is a prevalent issue in the United States. Excess body fat can contribute to a range of health problems, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hormonal disruptions. For men, the accumulation of visceral fat, which surrounds the abdominal organs, is particularly concerning as it can lead to insulin resistance and altered hormone levels.
The Hypothesis: A Vicious Cycle
The hypothesis posits that low libido and weight gain may form a vicious cycle, where one condition exacerbates the other. As men gain weight, their testosterone levels may decrease due to the conversion of testosterone to estrogen in fat tissue. This hormonal shift can lead to a reduced libido, which in turn may contribute to further weight gain. The lack of sexual activity and motivation to engage in physical exercise can perpetuate this cycle, leading to a decline in overall health.
Hormonal Mechanisms
The conversion of testosterone to estrogen in adipose tissue is a key mechanism in this hypothesis. As men gain weight, the enzyme aromatase, which is more active in fat cells, converts testosterone into estradiol, a form of estrogen. This process can lead to a relative increase in estrogen levels, which may further suppress testosterone production and contribute to low libido.
Psychological and Lifestyle Factors
Beyond hormonal changes, psychological and lifestyle factors play a significant role in the interplay between low libido and weight gain. Stress, depression, and anxiety can diminish sexual desire and lead to unhealthy eating habits and sedentary behavior. Conversely, the frustration and self-esteem issues associated with low libido may drive men to seek comfort in food, further contributing to weight gain.
Potential Interventions
Addressing the cycle of low libido and weight gain requires a multifaceted approach. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help men lose weight and improve their hormonal balance. Psychological support, including counseling and stress management techniques, can also be beneficial in addressing the emotional aspects of these conditions.
Medical Treatments
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary. Testosterone replacement therapy can be an option for men with clinically low testosterone levels, although it should be used cautiously and under medical supervision. Medications that target weight loss and improve metabolic health may also be considered, but their use should be carefully evaluated in the context of each individual's health profile.
Conclusion
The hypothesis linking low libido and weight gain in American males offers a valuable framework for understanding the complex interplay between sexual health and overall well-being. By recognizing the potential for these conditions to form a vicious cycle, healthcare providers can develop more effective strategies to help men break free from this pattern. Through a combination of lifestyle changes, psychological support, and targeted medical interventions, it is possible to improve both sexual health and overall quality of life for American males.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation
Dear Patient,
Once you have completing the above contact form, for security purposes and confirmation, please confirm your information by calling us.
Please call now: 1-800-380-5339.
Welcoming You To Our Clinic, Professor Tom Henderson.

- Revitalizing Intimacy: Strategies for Overcoming Low Libido in Long-term Relationships [Last Updated On: February 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 23rd, 2025]
- Revolutionizing the Approach to Low Libido: Proactive Medical Science at Work [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Comprehensive Analysis of Factors Influencing Male Libido: Psychological, Physiological, and Therapeutic Perspectives [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in Men: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring Hormonal Influences on Male Libido and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Low Libido in Men [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Managing Menopausal Libido: Understanding the Impact and Effective Solutions for Women's Health [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in Men: Causes, Impacts, and Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in Men: Psychological Factors and Practical Solutions [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link: Anxiety and Its Impact on Male Libido in the American Context [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Link Between Chronic Diseases and Low Libido in American Males [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Spectrum of Medical Therapies for Low Libido in Postpartum American Males [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring Treatments for Low Libido in American Males: Hormonal, Psychological, and Innovative Approaches [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Exploring Physical Causes of Low Libido in American Males: Hormones, Health, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Natural Supplements for Low Libido in Men: Scientific Insights and Clinical Evidence [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness Impact on Libido: Medical Insights and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Libido in Men: Causes, Medical Interventions, and Lifestyle Solutions [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Exploring Medical Causes and Solutions for Low Libido in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Medication-Induced Low Libido in American Men: Causes and Countermeasures [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Psychological Roots of Low Libido in American Males: Stress, Depression, and Beyond [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Diabetes and Libido: Understanding Impacts and Managing Low Sexual Desire in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Male Libido: Causes, Effects, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Exploring Low Libido in Men: Causes, Treatments, and Future Innovations [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Libido in Middle-Aged Men: Causes, Treatments, and Importance of Professional Help [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Men: Health Risks and Importance of Medical Intervention [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Libido and Depression: Understanding the Medical Connection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hyperthyroidism's Impact on Libido in American Males: Causes, Effects, and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Chronic Pain and Low Libido: Understanding the Medical Connection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Low Libido in American Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Low Libido in Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Postpartum Libido Decline in American Males: Causes and Multifaceted Solutions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Supporting Low Libido in Women Over 50: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Men: Causes, Impacts, and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Libido: Physiological, Psychological, and Relational Effects in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Effective Treatments for Low Libido in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding and Enhancing Low Libido in Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding and Supporting Low Libido in Lactating Women: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Risks, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Effective Medical Treatments for Boosting Libido in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sudden Low Libido in American Men: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Revitalizing Sexual Health: Understanding and Overcoming Low Libido in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Libido Treatments for American Males: Risks and Benefits Explored [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Males: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Males: Causes and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Post-Surgery Libido Recovery: Hormonal, Psychological, and Physical Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Males Post-Pregnancy: Causes, Impacts, and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Libido in Male Athletes: Causes, Effects, and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Women: Causes, Impacts, and Tailored Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Boosting Male Libido: Diet, Exercise, and Lifestyle Strategies for Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Chronic Low Libido in American Males: Medical Signs and Underlying Causes [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Age-Related Low Libido in American Men: Hormonal, Lifestyle, and Psychological Approaches [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Medical Patterns of Low Libido in Young American Males: Causes and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Libido in Male Surgical Patients: Physiological, Psychological, and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Effective Medical Strategies to Restore Libido in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Understanding and Revitalizing Low Libido in American Men: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Libido and Unhappiness in American Men: Causes, Impacts, and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Managing Low Libido in American Males Post-Chemotherapy: Medical and Lifestyle Approaches [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Hypertension's Impact on American Males' Libido: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in Women: Medical Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Understanding and Combating Low Libido in American Men: Medical Causes and Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Antidepressants and Low Libido in American Males: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Rising Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Males: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Understanding and Boosting Low Libido in American Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Libido in American Men: Impact of Medical Procedures and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Medical Factors Impacting Low Libido in Women Under 40: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Addressing Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Diagnostics, and Tailored Treatments [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Treatments, and Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Medical Causes of Persistent Low Libido in American Men: Hormones, ED, and More [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Medical Insights into Low Libido: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatments for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Low Libido in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Males: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]